Table of Contents
Toggle Shadow Health Focused Abdominal Assessment With Esther
Shadow Health Focused Abdominal Assessment With Esther
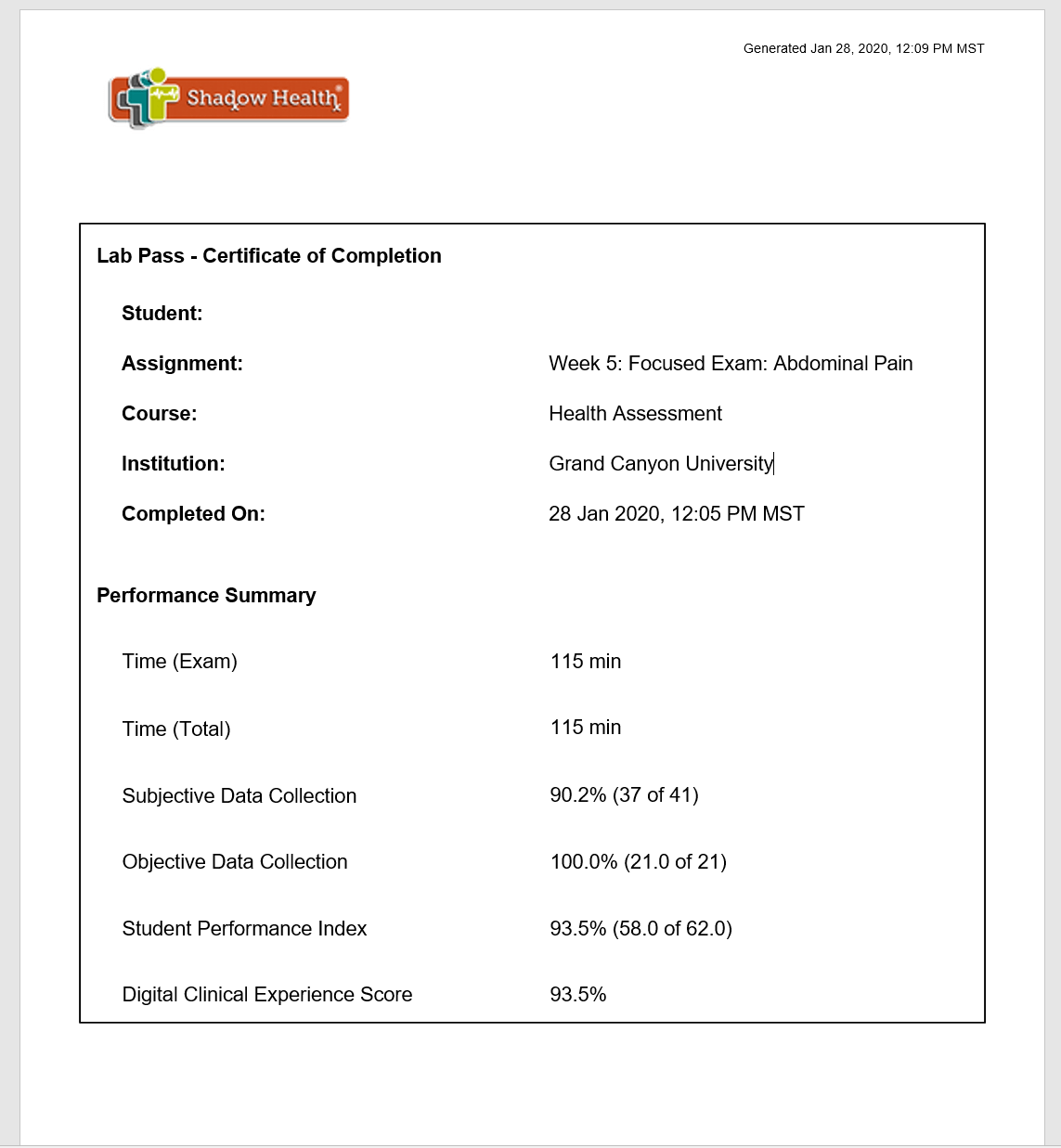
This clinical experience is a focused exam. Students have one opportunity to complete this assignment and score at the Proficiency level. Upon completion, submit the lab pass to the instructor in the classroom.
Students successfully scoring within the Proficiency level in the Digital Clinical Experience will earn a grade of 100 points. Students who do not pass the performance-based assessment and scoring within the Proficiency level will receive a failing grade (68 points).
Please review the assignment in the Health Assessment Student Handbook in Shadow Health prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
You are not required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite.
Expert Answer
Place your order now for a similar assignment and get fast, cheap and best quality work written by our expert level assignment writers. Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order

Shadow Health Focused Abdominal Assessment With Esther
The Shadow Health focused abdominal assessment is a critical virtual simulation that helps nursing students develop essential clinical skills through realistic patient interactions. Shadow Health Digital Clinical Experiences™ are a vital part of the education of more than 700,000 nursing students across the country, making it one of the most widely used virtual simulation platforms in nursing education.
Key Learning Objectives
The Shadow Health abdominal pain focused exam with Esther Park is designed to help students master:
- Comprehensive health history taking techniques
- Physical assessment skills specific to abdominal complaints
- Clinical reasoning and diagnostic thinking
- Therapeutic communication with elderly patients
- Professional documentation standards
Why This Assessment Matters
Research shows that Shadow Health Digital Clinical Experiences™ help 82% of learners increase efficiency in clinical skills development. The program specifically improves:
| Skill Area | Improvement Rate | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | 82% | Enhanced patient history accuracy |
| Therapeutic Communication | 78% | Better patient rapport |
| Care Planning | 75% | More comprehensive care strategies |
| Clinical Reasoning | 73% | Improved diagnostic thinking |
Source: Elsevier Education Research, 2023
Understanding Esther Park Case Study {#esther-park-case}
Patient Background
Esther Park is a 78-year-old Korean-American woman presenting with abdominal pain. Understanding her demographic and cultural background is crucial for providing culturally competent care.
Key Patient Demographics:
- Age: 78 years old
- Gender: Female
- Ethnicity: Korean-American
- Chief Complaint: Abdominal pain (6/10 severity)
- Associated Symptoms: Bloating, decreased appetite
Clinical Presentation Overview
Students encounter Esther Park in a simulated clinical environment where she presents with:
Primary Symptoms:
- Abdominal pain rated 6/10
- Bloating sensation
- Decreased appetite
- Concerns about bowel changes
Assessment Findings:
- Tender abdominal mass in lower left quadrant
- Vital signs within normal limits for age
- Patient appears uncomfortable but cooperative
Cultural Considerations
When conducting the Shadow Health Esther Park assessment, students must consider:
- Language barriers and communication preferences
- Cultural attitudes toward pain expression
- Family involvement in healthcare decisions
- Traditional health beliefs that may influence symptoms reporting
Step-by-Step Assessment Guide {#assessment-guide}
Pre-Assessment Preparation
Before beginning your shadow health focused exam abdominal pain simulation:
- Review anatomy and physiology of the gastrointestinal system
- Practice communication techniques for elderly patients
- Understand cultural competency basics
- Prepare assessment tools and documentation materials
Systematic Assessment Approach
1. Subjective Data Collection
History of Present Illness (HPI) Focus on the OLDCARTS method:
- Onset: When did the pain begin?
- Location: Where exactly is the pain?
- Duration: How long does it last?
- Character: What does the pain feel like?
- Aggravating factors: What makes it worse?
- Relieving factors: What helps?
- Timing: Is there a pattern?
- Severity: Rate the pain 1-10
Key Questions for Esther Park:
- “Can you describe your abdominal pain?”
- “What makes the pain better or worse?”
- “Have you noticed any changes in your bowel movements?”
- “Are you taking any medications?”
2. Objective Data Collection
Apply the 4 basic components of the abdominal exam—inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation.
Assessment Order (Critical for Abdomen):
- Inspection – Visual examination first
- Auscultation – Listen before touching
- Percussion – Light tapping for organ boundaries
- Palpation – Physical examination last
Detailed Assessment Techniques
Inspection
- Patient positioning: Supine with knees slightly bent
- Abdominal contour: Note symmetry, distention
- Skin integrity: Check for scars, rashes, masses
- Umbilicus: Assess for hernias or discharge
Auscultation
- Bowel sounds: All four quadrants (5 minutes minimum)
- Vascular sounds: Listen for bruits
- Frequency: Normal, hyperactive, or hypoactive
Percussion
- Organ boundaries: Liver span, spleen size
- Fluid detection: Shifting dullness for ascites
- Air-filled areas: Tympanic sounds over intestines
Palpation
When palpating the abdomen, ask the patient to bend their knees when lying in a supine position to enhance relaxation of abdominal muscles.
Light Palpation:
- Assess all quadrants systematically
- Note tenderness, masses, or organ enlargement
- Important: Palpate painful areas last
Deep Palpation:
- Deeper assessment of organs
- Check for rebound tenderness
- Assess for guarding or rigidity
Clinical Documentation and SOAP Notes
SOAP Note Structure for Esther Park
Subjective
Chief Complaint: “I’ve been having stomach pain for the past few days.”
History of Present Illness:
- 78-year-old Korean-American female
- Abdominal pain onset 3 days ago
- Pain located in lower left quadrant
- Described as “cramping” and constant
- Severity 6/10
- Associated with bloating and decreased appetite
- No fever, nausea, or vomiting reported
Objective
Vital Signs:
- BP: 142/88 mmHg
- HR: 76 bpm
- RR: 18/min
- Temp: 98.6°F
- Pain: 6/10
Physical Assessment:
- General appearance: Alert, oriented, appears uncomfortable
- Abdomen: Soft, non-distended, bowel sounds present
- Tender mass palpated in LLQ
- No rebound tenderness or guarding
- No hepatosplenomegaly
Assessment
Primary Diagnosis Considerations:
- Possible diverticulitis
- Rule out bowel obstruction
- Consider inflammatory bowel disease
Plan
Diagnostic:
- Complete blood count
- Comprehensive metabolic panel
- CT scan of abdomen/pelvis
- Urinalysis
Therapeutic:
- NPO status initially
- IV hydration
- Pain management
- Monitor vital signs
Documentation Best Practices
| Element | Best Practice | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|
| Subjective | Use patient’s exact words | Interpreting patient statements |
| Objective | Include measurable data | Subjective observations in objective |
| Assessment | Evidence-based conclusions | Jumping to conclusions |
| Plan | Specific, measurable goals | Vague treatment plans |
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Communication Barriers
Problem: Language and cultural differences affecting assessment quality
Solutions:
- Use simple, clear language
- Allow extra time for responses
- Respect cultural pain expressions
- Consider family member interpretation (with patient consent)
Challenge 2: Incomplete Data Collection
Problem: Missing critical assessment components
Solutions:
- Follow systematic assessment order
- Use assessment checklists
- Practice active listening techniques
- Review missed questions during simulation
Challenge 3: Clinical Reasoning Difficulties
Problem: Struggling to connect assessment findings
Solutions:
- Review pathophysiology before simulation
- Practice differential diagnosis thinking
- Use concept mapping techniques
- Discuss findings with instructors
Performance Optimization Tips
Pre-Simulation:
- Review case materials thoroughly
- Practice assessment techniques
- Understand scoring criteria
- Prepare question lists
During Simulation:
- Take time to think before responding
- Use therapeutic communication
- Follow systematic assessment order
- Document findings accurately
Post-Simulation:
- Review performance feedback
- Identify knowledge gaps
- Practice weak areas
- Seek instructor guidance
Study Resources and Practice Tips {#study-resources}
Essential Study Materials
Textbook Resources:
- Health Assessment nursing textbooks
- Pathophysiology references
- Cultural competency guides
- Documentation standards
Online Resources:
- Lecturio Nursing abdominal assessment guides with free cheat sheets
- NCBI nursing skills bookshelf
- Professional nursing organization websites
- Peer-reviewed research articles
Practice Techniques
Flashcard Topics
Create flashcards covering:
- Anatomy and physiology terminology
- Assessment techniques and sequences
- Normal vs. abnormal findings
- Cultural considerations for elderly Korean patients
- Documentation requirements and formats
Study Group Activities
- Role-play scenarios with classmates
- Case study discussions and analysis
- Peer teaching of assessment techniques
- Group review of documentation standards
Time Management Strategies
| Phase | Time Allocation | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-simulation | 30-45 minutes | Review case, practice questions |
| Simulation | 45-60 minutes | Complete assessment systematically |
| Post-simulation | 15-30 minutes | Review performance, document learning |
Advanced Clinical Considerations {#advanced}
Geriatric Assessment Modifications
When working with elderly patients like Esther Park, consider:
Physical Modifications:
- Allow more time for position changes
- Provide additional support during examination
- Consider joint limitations and mobility issues
- Be gentle with palpation techniques
Communication Adaptations:
- Speak clearly and at appropriate volume
- Allow processing time for questions
- Repeat important information
- Confirm understanding frequently
Evidence-Based Practice Integration
Recent research shows statistically significant improvements in clinical reasoning and communication variables with virtual patient simulation, supporting the effectiveness of Shadow Health assessments in nursing education.
Key Research Findings:
- Student confidence increases with repeated practice
- Clinical reasoning skills improve significantly
- Communication abilities show measurable enhancement
- Assessment accuracy increases with structured approaches
Technology and Platform Tips {#technology}
Shadow Health Platform Navigation
Login and Setup:
- Ensure stable internet connection
- Use compatible browser (Chrome recommended)
- Test audio/video settings
- Review technical requirements
During Assessment:
- Save progress frequently
- Use help features when available
- Review scoring rubrics
- Take advantage of retry opportunities
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Audio problems | Check browser permissions, restart session |
| Slow loading | Clear browser cache, check internet speed |
| Lost progress | Contact technical support, save frequently |
| Scoring questions | Review rubrics, seek instructor clarification |
Professional Development Impact {#professional-impact}
Career Preparation Benefits
The Shadow Health abdominal pain assessment prepares students for:
Clinical Practice:
- Real patient interactions
- Time management skills
- Professional communication
- Accurate documentation
NCLEX Preparation:
- Assessment technique questions
- Clinical reasoning scenarios
- Priority-setting situations
- Cultural competency items
Future Specialization:
- Gastroenterology nursing
- Emergency department skills
- Medical-surgical competencies
- Geriatric care expertise
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does the Shadow Health Esther Park assessment take?
A: Typically 45-60 minutes for completion, with additional time for review and documentation.
Q: Can I retake the assessment if I don’t perform well?
A: Most programs allow retakes, but policies vary by institution. Check with your instructor for specific guidelines.
Q: What’s the most important aspect of the abdominal assessment?
A: Following the correct sequence (inspect, auscultate, percuss, palpate) and maintaining therapeutic communication throughout.
Q: How can I improve my cultural competency for this case?
A: Study Korean cultural health beliefs, practice respectful communication, and consider family dynamics in healthcare decisions.
Q: What are common mistakes students make?
A: Rushing through questions, palpating before auscultating, missing cultural cues, and incomplete documentation.
Conclusion
The Shadow Health focused abdominal assessment with Esther provides invaluable learning opportunities for nursing students. Success requires thorough preparation, systematic assessment techniques, cultural sensitivity, and professional documentation skills.
By following this comprehensive guide, students can maximize their learning experience and develop the clinical competencies essential for professional nursing practice. Remember that virtual simulations like Shadow Health are designed to enhance, not replace, real clinical experiences, preparing students for the complexities of modern healthcare delivery.
Key Takeaways:
- Practice systematic assessment techniques
- Develop cultural competency skills
- Master therapeutic communication
- Perfect documentation standards
- Embrace continuous learning opportunities
For additional support and resources, consult your nursing faculty, utilize institutional learning resources, and engage with professional nursing organizations to enhance your educational journey.
References
- Elsevier Education. (2024). Nursing Simulation for Nursing students | Shadow Health. Retrieved from https://evolve.elsevier.com/education/simulations/shadow-health/
- ScienceDirect. (2024). Navigating the Virtual Frontier: A Virtual Patient Simulation Pilot Study in Prelicensure Baccalaureate Nursing Education. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1876139924000811
- NCBI Bookshelf. (2024). Abdominal Examination – StatPearls. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459220/
- NCBI Bookshelf. (2023). Chapter 12 Abdominal Assessment – Nursing Skills. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK593213/
- Lecturio Nursing. (2024). Abdominal Assessment [+ Free Cheat Sheet]. Retrieved from https://www.lecturio.com/nursing/free-cheat-sheet/abdominal-assessment-order-tips/
- Nursing Times. (2024). How to assess and examine a patient with abdominal symptoms. Retrieved from https://www.nursingtimes.net/assessment-skills/how-to-assess-and-examine-a-patient-with-abdominal-symptoms-29-07-2024/
- Elsevier Education. (2023). Shadow Health – Research & Articles. Retrieved from https://evolve.elsevier.com/education/simulations/shadow-health/research/
- Clinical Simulation In Nursing. (2014). Transformative Learning through Virtual Patient Simulations: Predicting Critical Student Reflections. Retrieved from https://www.nursingsimulation.org/article/S1876-1399(14)00030-9/fulltext

I am a professional nursing assignment expert offering comprehensive academic support to university nursing students across various institutions. My services are designed to help learners manage their workload effectively while maintaining academic excellence. With years of experience in nursing research, case study writing, and evidence-based reporting, I ensure every paper is original, well-researched, and aligned with current academic standards.
My goal is to provide dependable academic assistance that enables students to focus on practical training and career growth.
Contact me today to receive expert guidance and timely, high-quality nursing assignment help tailored to your academic needs.


