
Shadow Health Comprehensive Assessment of Tina
Complete the Digital Experience. The estimated average time to complete this assignment each time is 3 hours and 30 minutes. Please note, this is an average time. Some students may need longer.
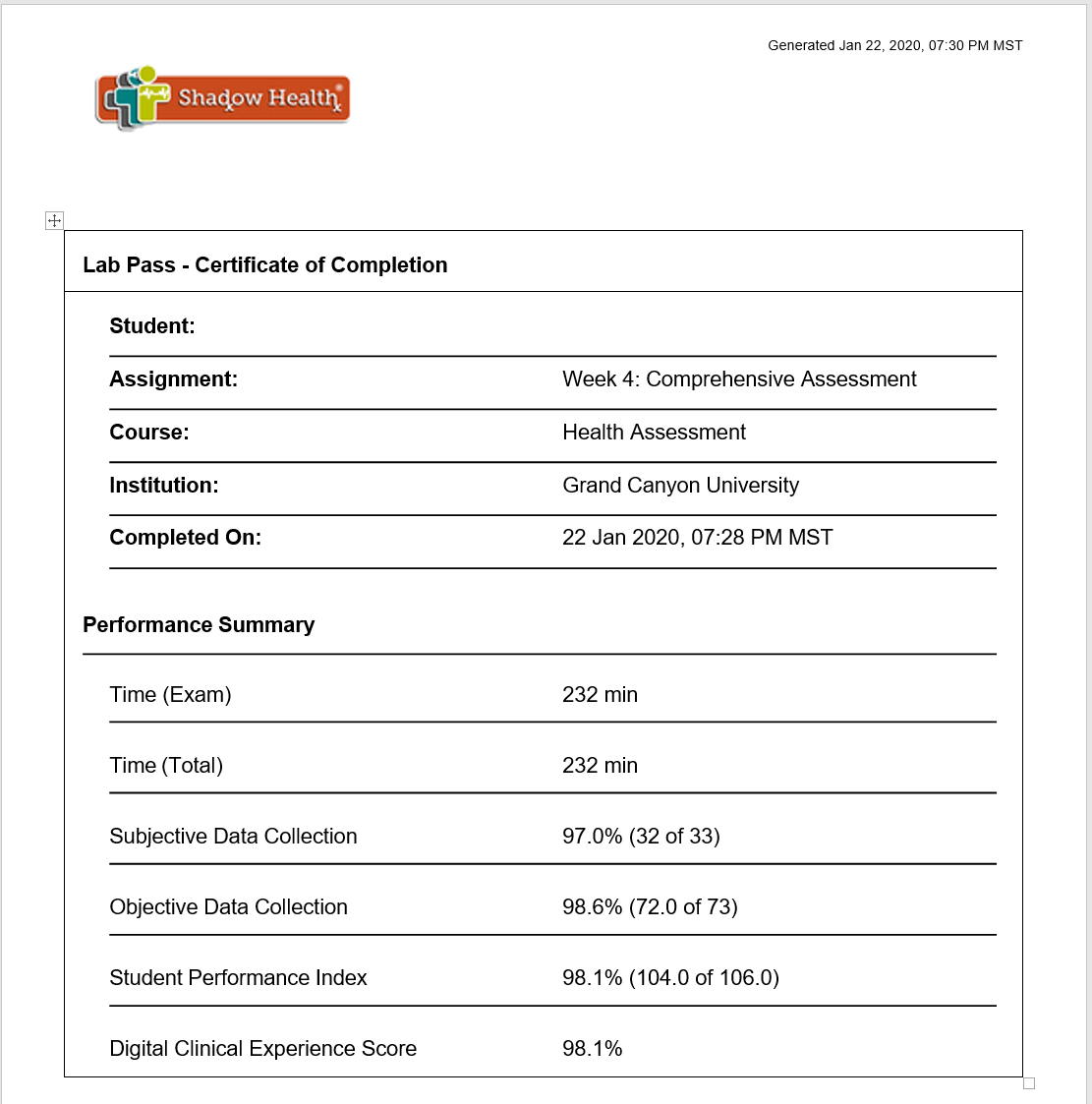
This clinical experience is a comprehensive exam. Students must score at the level of “Proficiency” in the Shadow Health Digital Clinical Experience. Students have three opportunities to complete this assignment and score at the Proficiency level. Upon completion, submit your lab pass to your instructor in the classroom.
Students successfully scoring within the Proficiency level in the Digital Clinical Experience on the first attempt will earn a grade of 150 points; students successfully scoring at the Proficiency level on the second attempt will earn a grade of 135 points; and students successfully scoring at the Proficiency level on the third attempt will earn a grade of 120 points. Students who do not pass the performance-based assessment by scoring within the Proficiency level in three attempts will receive a failing grade (102 points).
Please review the assignment in the Health Assessment Student Handbook in Shadow Health prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
If Proficiency is not achieved on the first attempt it is recommended that you review your answers with the correct answers on the Experience Overview page. Review the report by clicking on each tab to the left titled; Transcript, Subjective Data Collection, Objective Data Collection, Documentation, and SBAR to compare your work. Reviewing this overview and course resources may help you improve your score.
You are not required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite.
Expert Answer
Place your order now for a similar assignment and get fast, cheap and best quality work written by our expert level assignment writers. Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order

What is Shadow Health Assessment?
Introduction
In the world of healthcare and nursing education, new technologies are constantly emerging to enhance patient care and improve training methodologies. One such innovative tool is Shadow Health Assessment. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of what Shadow Health Assessment is, its benefits, how it works, its importance in healthcare, its applications in nursing education, its limitations, and future trends.
Understanding Shadow Health Assessment
Shadow Health Assessment is a virtual patient simulation platform that enables healthcare professionals and students to engage in realistic clinical scenarios. It is an interactive, web-based learning environment designed to replicate real-life patient interactions. Through this assessment, users can develop critical thinking skills, clinical reasoning abilities, and improve their overall competence in patient care.
Benefits of Shadow Health Assessment
- Realistic Patient Encounters: Shadow Health Assessment offers realistic virtual patients with diverse backgrounds, medical histories, and symptoms. This allows healthcare professionals and students to practice their skills in a safe and controlled environment.
- Active Learning: Users actively engage in patient assessments, health histories, physical examinations, and clinical reasoning, promoting active learning and knowledge retention.
- Immediate Feedback: The platform provides immediate feedback and performance evaluations, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement.
- Flexibility and Accessibility: Shadow Health Assessment can be accessed anytime, anywhere, making it convenient for healthcare professionals and students to enhance their skills and knowledge.
- Standardized Assessment: The virtual patient scenarios provide standardized assessments, ensuring consistency and fairness in evaluating competency levels.
How Shadow Health Assessment Works
Shadow Health Assessment utilizes advanced technology to create immersive virtual patient experiences. Users interact with virtual patients through various modules, including health history interviews, physical assessments, documentation, and diagnostic reasoning. The platform simulates the entire patient encounter, allowing users to apply their knowledge and skills in a practical setting.
The Importance of Shadow Health Assessment in Healthcare
Shadow Health Assessment plays a vital role in healthcare for both professionals and students. It provides an opportunity to refine clinical skills, enhance critical thinking abilities, and improve patient care. By practicing in a risk-free environment, healthcare professionals can gain confidence and competence in their diagnostic and treatment decisions, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Shadow Health Assessment in Nursing Education
Nursing education greatly benefits from the integration of Shadow Health Assessment. It allows students to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and clinical practice. By engaging in virtual patient encounters, nursing students develop essential assessment and communication skills, empowering them to deliver high-quality care in real-life settings.
Limitations of Shadow Health Assessment
While Shadow Health Assessment offers significant advantages, it also has certain limitations. Some of these limitations include:
- Lack of Human Interaction: Virtual patient encounters cannot fully replace the experience of interacting with real patients, including the nuances of non-verbal communication and patient-provider rapport.
- Limited Physical Examination: While virtual patient simulations cover a wide range of scenarios, they may not fully capture the complexity and variability of physical examinations.
- Technology Requirements: Access to the platform relies on technology and internet connectivity, which may pose challenges in resource-constrained environments.
Future Trends in Shadow Health Assessment
As technology continues to advance, Shadow Health Assessment is expected to evolve and incorporate new features. Some future trends in this field may include:
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI algorithms can enhance the realism and interactivity of virtual patient encounters, providing more sophisticated feedback and adaptive learning experiences.
- Expanded Specialty Areas: The platform may expand its scope to include a wider range of specialty areas, allowing healthcare professionals and students to practice in specific clinical contexts.
- Enhanced Interactivity: Future developments may include more immersive and interactive elements, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, to create even more realistic simulations.
Conclusion
Shadow Health Assessment is a powerful tool in healthcare and nursing education that offers realistic virtual patient encounters. It provides numerous benefits, including active learning, immediate feedback, flexibility, and standardized assessments. While it has certain limitations, its importance in enhancing clinical skills and patient care cannot be understated. As technology progresses, we can expect to see even more advanced features and applications in the future.
FAQs
Can Shadow Health Assessment replace real patient interactions?
While Shadow Health Assessment offers a realistic learning experience, it cannot fully replace the value of interacting with real patients. It should be seen as a supplementary tool to enhance clinical skills.
Is Shadow Health Assessment accessible from any device?
Yes, Shadow Health Assessment is a web-based platform and can be accessed from various devices with internet connectivity.
Does Shadow Health Assessment provide certifications?
Shadow Health Assessment itself does not provide certifications. However, it can be used as a training tool to develop competence and prepare for certification exams.
Can Shadow Health Assessment be customized for specific healthcare specialties?
While the platform currently focuses on general healthcare scenarios, there are possibilities for customization and expansion into specific specialty areas in the future.
How does Shadow Health Assessment benefit nursing students?
Shadow Health Assessment allows nursing students to practice essential assessment and communication skills in a realistic virtual environment, bridging the gap between theory and practice.

How do you perform a complete head to toe assessment?
Performing a complete head-to-toe assessment is a comprehensive process used by healthcare professionals to evaluate a patient’s overall health status. It involves systematically examining various body systems from head to toe to identify any abnormalities or potential health issues. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to perform a complete head-to-toe assessment:
- Introduction and Preparation
- Introduce yourself to the patient and explain the purpose of the assessment.
- Ensure privacy and provide a comfortable environment for the patient.
- Wash your hands or use hand sanitizer to maintain proper hygiene.
- General Observation
- Observe the patient’s general appearance, noting their posture, body movements, and overall level of consciousness.
- Assess for signs of distress, discomfort, or pain.
- Note any visible abnormalities, such as skin rashes, scars, or wounds.
- Vital Signs
- Measure and record the patient’s vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature.
- Assess oxygen saturation levels using a pulse oximeter.
- Head and Neck Assessment
-
- Inspect and palpate the head, noting any lumps, tenderness, or deformities.
- Assess the scalp, hair, and facial features for any abnormalities.
- Examine the neck for swollen lymph nodes, stiffness, or masses.
- Assess the thyroid gland by palpating for enlargement or nodules.
- Eyes
- Test visual acuity using a Snellen chart or other appropriate tools.
- Inspect the external eye structures for redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Evaluate pupillary response to light and accommodation.
- Perform a fundoscopic examination to assess the retina and optic disc.
- Ears, Nose, and Throat
- Inspect the external ears for abnormalities, such as inflammation or discharge.
- Assess auditory acuity using a tuning fork or whisper test.
- Examine the nasal cavity for any signs of congestion, discharge, or polyps.
- Inspect the oral cavity for lesions, ulcers, or abnormalities in the teeth and gums.
- Evaluate the throat for redness, tonsillar enlargement, or signs of infection.
- Respiratory System
- Auscultate lung sounds in all lung fields using a stethoscope.
- Observe for any signs of respiratory distress or abnormal breathing patterns.
- Assess respiratory effort, chest symmetry, and the presence of cough or sputum.
- Cardiovascular System
- Auscultate heart sounds using a stethoscope, including the four cardiac areas (aortic, pulmonic, tricuspid, and mitral).
- Palpate peripheral pulses (e.g., radial, brachial, femoral) and assess their strength and regularity.
- Measure and assess the ankle-brachial index (ABI) to evaluate peripheral vascular status.
- Check for the presence of edema in the lower extremities.
- Abdominal Assessment
-
- Inspect the abdomen for any visible abnormalities, scars, or distention.
- Palpate the abdomen gently to assess for tenderness, masses, or organ enlargement.
- Auscultate bowel sounds in all quadrants using a stethoscope.
- Assess liver and spleen size and tenderness, if necessary.
- Musculoskeletal System
- Observe the patient’s posture, gait, and coordination.
- Assess joint range of motion and note any swelling, tenderness, or deformities.
- Palpate muscles and bones for tenderness, crepitus, or abnormalities.
- Neurological Assessment
- Assess the patient’s level of consciousness, orientation, and cognitive function.
- Evaluate cranial nerves by performing specific tests for each nerve.
- Test sensory function, motor strength, and coordination.
- Assess reflexes, including deep tendon reflexes and plantar reflexes.
- Integumentary System
- Inspect the skin for color, moisture, temperature, and any lesions or abnormalities.
- Assess skin turgor and elasticity.
- Perform a thorough skin assessment, paying attention to pressure ulcers or areas of skin breakdown.
- Genitourinary System
- Inquire about any urinary symptoms, such as frequency, urgency, or pain.
- Assess urine output and characteristics if necessary.
- In male patients, inspect the external genitalia for abnormalities.
- In female patients, assess the external genitalia and perform a pelvic examination if indicated.
- Documentation
- Record all findings accurately and in a systematic manner.
- Document any abnormal or significant findings that require further investigation or follow-up.
What are the steps in health assessment?
A health assessment is a systematic process used to gather information about a person’s overall health status, including physical, mental, and social aspects. It involves various steps to obtain a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s health. Here are the steps typically followed in a health assessment:
- Introduction and Preparation
- Introduce yourself to the person and explain the purpose of the health assessment.
- Establish rapport and ensure privacy and confidentiality.
- Obtain informed consent from the person, explaining the nature of the assessment.
- Health History
- Gather information about the person’s medical history, including past illnesses, surgeries, and chronic conditions.
- Inquire about current symptoms, allergies, medications, and immunization history.
- Explore the person’s family medical history to identify any genetic predispositions or hereditary conditions.
- Obtain details about the person’s lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, smoking, alcohol consumption, and substance use.
- Physical Examination
- Perform a comprehensive physical examination, which may include:
- Measurement of vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature.
- Inspection of the person’s general appearance, skin, and body systems.
- Palpation to assess the texture, temperature, tenderness, and organ size.
- Percussion to evaluate the sounds produced by tapping on body surfaces.
- Auscultation using a stethoscope to listen to internal body sounds, such as heart and lung sounds.
- Perform a comprehensive physical examination, which may include:
- Assessment of Body Systems
- Assess each body system to identify any abnormalities or potential health issues. This may include:
- Respiratory system assessment (breathing, lung sounds, etc.).
- Cardiovascular system assessment (heart sounds, pulses, etc.).
- Gastrointestinal system assessment (abdominal exam, bowel sounds, etc.).
- Musculoskeletal system assessment (range of motion, strength, etc.).
- Neurological system assessment (mental status, reflexes, etc.).
- Integumentary system assessment (skin condition, lesions, etc.).
- Genitourinary system assessment (urinary symptoms, reproductive health, etc.).
- Psychosocial assessment (mental health, social support, etc.).
- Assess each body system to identify any abnormalities or potential health issues. This may include:
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests
- Order and interpret relevant laboratory tests, such as blood tests, urine analysis, and imaging studies, based on the person’s health history and physical examination findings.
- Consider other specialized tests or consultations if needed, depending on specific concerns or symptoms.
- Health Promotion and Education
- Provide health education and counseling based on the person’s individual needs and identified risk factors.
- Discuss preventive measures, lifestyle modifications, and strategies for managing existing health conditions.
- Encourage regular screenings and immunizations as appropriate.
- Documentation
- Document all findings, including the health history, physical examination findings, laboratory test results, and the plan of care.
- Use a standardized format or electronic health record system to ensure accuracy and clarity.
- Follow-up and Referrals
- Schedule follow-up appointments or referrals to other healthcare professionals, specialists, or support services if necessary.
- Coordinate care and ensure continuity for ongoing management of health conditions.
Shadow Health Comprehensive Assessment
Shadow Health comprehensive assessment represents a revolutionary approach to healthcare education and patient evaluation, combining advanced simulation technology with evidence-based clinical practices. This comprehensive evaluation method has transformed how healthcare professionals approach patient care, offering an immersive learning environment that mirrors real-world clinical scenarios.
Understanding the Shadow Health Platform
The Shadow Health comprehensive assessment platform utilizes sophisticated virtual patient simulations to create realistic healthcare encounters. Healthcare professionals and students can hover over the patient data items below to reveal important information including pro tips and example questions, enabling them to develop critical thinking skills essential for clinical practice. This interactive approach ensures that learners engage with authentic patient presentations while receiving guided support throughout the assessment process.
Essential Components of Patient Interviews
Clinical experts selected these topics as essential components of a strong thorough interview with this patient. The comprehensive nature of Shadow Health assessments requires healthcare providers to address multiple aspects of patient care, from immediate concerns to long-term health management strategies. Each virtual encounter presents unique challenges that mirror the complexity of real patient interactions.
Medication History and Management
A crucial element of any comprehensive assessment involves detailed medication reconciliation. Patients often present with complex medication regimens that require careful evaluation. For instance, a patient might report taking drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol po qd last use this morning as part of their contraceptive management. This information becomes particularly relevant when the visit was annual gynecological examination, as healthcare providers must assess both efficacy and potential side effects of hormonal contraceptives.
The assessment process also includes evaluating other medications such as metformin 850 mg po bid last use this morning for patients who manage diabetes. Understanding medication timing, adherence, and patient knowledge about their prescriptions forms a fundamental component of comprehensive care. Additionally, respiratory medications like fluticasone propionate 110 mcg 2 puffs bid last use this morning require evaluation for proper technique and effectiveness, especially when patients also use rescue medications like a proventil inhaler.
Comprehensive Physical Examination Protocols
The general physical examination within Shadow Health comprehensive assessments follows systematic protocols that ensure thorough evaluation of all body systems. Healthcare providers learn to conduct focused examinations while maintaining awareness of interconnected health issues. For example, when evaluating a patient’s endocrine system, practitioners might note that the thyroid smooth without nodules no goiter, which provides important baseline information for ongoing health monitoring.
Reproductive Health Considerations
Annual gynecological examinations represent critical opportunities for comprehensive health assessment. These encounters often reveal important information about patients’ reproductive health choices, including the use of prescription birth control pills. Healthcare providers must be prepared to discuss contraceptive options, side effects, and alternative methods based on individual patient needs and preferences.
The timing of contraceptive use often becomes relevant during these assessments. For instance, understanding that a patient has been using birth control 4 months provides context for evaluating both effectiveness and any emerging side effects. This information helps guide clinical decision-making and patient education efforts.
Social and Lifestyle Factors
Shadow Health comprehensive assessments emphasize the importance of understanding patients’ social contexts and lifestyle factors. Patients may share that they socialize before and after church, indicating strong community connections that can impact health behaviors and support systems. Understanding that church especially is all working in their lives provides insight into potential resources for health promotion and disease management.
However, comprehensive assessments also reveal lifestyle factors that may impact health outcomes. Some patients acknowledge past substance use, stating they smoked pot since i was twenty, which requires sensitive discussion about current use patterns and potential health implications. Healthcare providers must approach these conversations with empathy while gathering necessary information for comprehensive care planning.
Temporal Aspects of Care
The timing of healthcare encounters plays a crucial role in comprehensive assessment. Understanding that months ago when she received previous care helps establish continuity and identify gaps in healthcare delivery. This temporal awareness enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions about screening intervals, follow-up appointments, and preventive care measures.
Technology Integration in Patient Care
Modern healthcare delivery increasingly relies on integrated technology platforms that support comprehensive patient assessment. Each visit to a healthcare facility now involves multiple data points that must be synthesized to create complete patient profiles. Shadow Health comprehensive assessment platforms prepare healthcare providers to navigate these complex information systems while maintaining focus on patient-centered care.
Educational Implications
The Shadow Health comprehensive assessment methodology has significant implications for healthcare education. By providing realistic patient scenarios that incorporate multiple health issues, medication regimens, and social factors, these platforms prepare future healthcare providers for the complexity of modern clinical practice. Students learn to synthesize information from multiple sources while developing essential communication and clinical reasoning skills.
Conclusion
Shadow Health comprehensive assessment represents a paradigm shift in healthcare education and patient evaluation. By incorporating realistic patient scenarios, complex medication regimens, and multifaceted health issues, these platforms prepare healthcare providers to deliver comprehensive, patient-centered care. The integration of technology with evidence-based clinical practices ensures that healthcare professionals develop the skills necessary to navigate the complexities of modern healthcare delivery while maintaining focus on individual patient needs and outcomes.
As healthcare continues to evolve, comprehensive assessment methodologies like those offered by Shadow Health will play increasingly important roles in preparing healthcare providers for successful clinical practice. The emphasis on thorough evaluation, patient interaction, and clinical reasoning ensures that future healthcare professionals are well-equipped to address the diverse and complex needs of their patients in various healthcare settings.

I am a professional nursing assignment expert offering comprehensive academic support to university nursing students across various institutions. My services are designed to help learners manage their workload effectively while maintaining academic excellence. With years of experience in nursing research, case study writing, and evidence-based reporting, I ensure every paper is original, well-researched, and aligned with current academic standards.
My goal is to provide dependable academic assistance that enables students to focus on practical training and career growth.
Contact me today to receive expert guidance and timely, high-quality nursing assignment help tailored to your academic needs.


