You are participating in the customization and implementation of a barcode medication administration system. In a 500-word APA essay, analyze how the process flow
You are participating in the customization and implementation of a barcode medication administration system. In a 500-word APA essay, analyze how the process flow will change from the current manual process to a barcode process and identify potential problem areas and possible solutions. Additionally, include a workflow diagram (Process Flowchart) from the manual process to the barcode process.
The resources to get started on this project are in the Additional Resources for this module.
REQUIRED SOURCE
McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. (2017). Nursing Informatics and the Foundation of Knowledge (4th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning. ISBN: 978-1284121247.
Assignment Expectations
Length: 500 words; answers must thoroughly address the questions in a clear, concise manner.
Structure: Include a title page and reference page in APA style. These do not count towards the minimum word count for this assignment.
References: Use the appropriate APA style in-text citations and references for all resources utilized to answer the questions. Include at least three (3) scholarly sources to support your claims.
Format: Save your assignment as a Microsoft Word document (.doc or .docx).
Expert Answer and Explanation
The Customization and Implementation of a Barcode Medication Administration System
Healthcare barcode solutions are vital when it comes to providing safe and quality data. Wilson et al. (2020) note that barcode solutions help track patient medication, modernize the patient admission procedure, track patient admission, and identify the clients when they are in hospital. The barcode system can also reduce medical errors by ensuring that the nurses administer the right medication. The purpose of this assignment is to analyze how my organization’s flow process with the transition from the current manual to a barcode process, and identify the potential problem areas and solutions.
Analysis of the Current Process
The current process is a manual process where information is processed manually. The majority of the activities are done manually with paper and pen. For instance, when a patient enters the hospital, they will be admitted manually and their names entered into the system using pen and paper (Samadbeik et al., 2017). Also, in the current process, the input is collected in a tray and the person in charge is required to apply their brain to reply to the inquiries.
This type of data management can encourage medical errors, especially when the person making data entry is exhausted or tired. For instance, the nurse at the admission point can mistype the name of the patient, hence leading to a medication administration error. Patient privacy can also be breached if data in the “tray” or the file cabinet is accessed by unauthorized individuals. Manual data management is tiring because it involves repeating the same process many times.
Manual data processing also takes too much space (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2017). Hospitals applying this process need a huge scape to design file cabinets that can be used to store data. Information in manual data processing can easily be lost or damaged. Making changes to data created by hand is hard and this can create a lot of inconveniences.
Diagram of the New Process
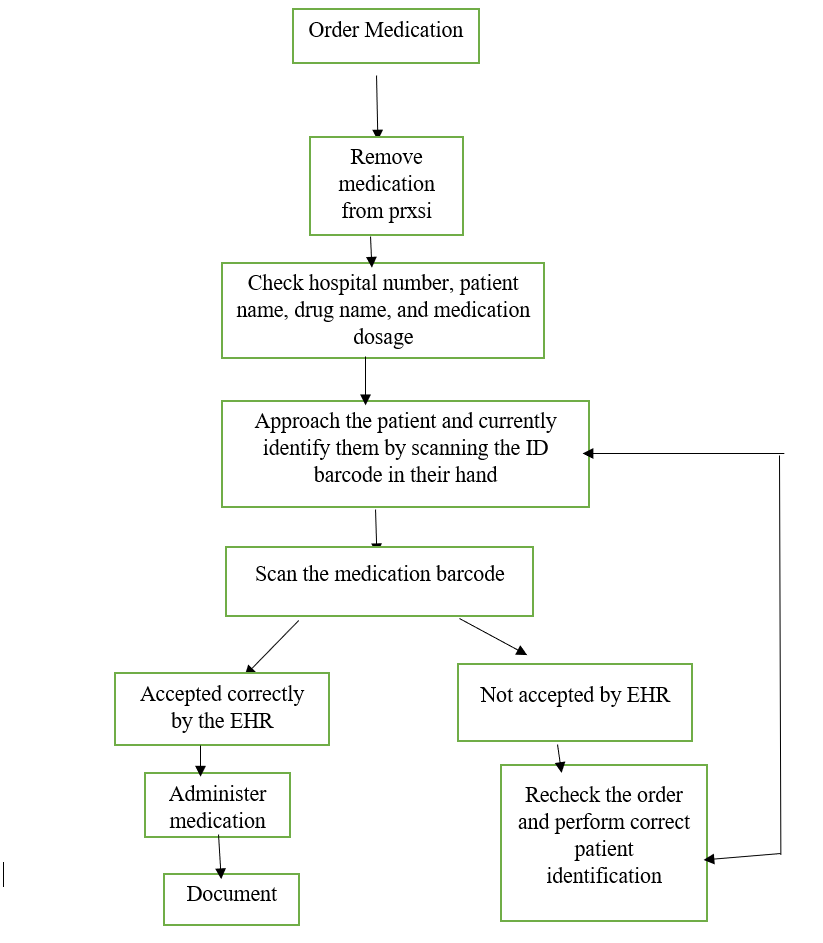
Discussion of the New Process
Healthcare professionals have been developing electronic data management systems to solve the flaws in the manual data processing system. Barcode system that solves most of the flaws experienced in manual data processing. As seen in the diagram above, the barcode system can help a nurse determine whether the medication provided by the pharmacists is indeed prescribed to a specific patient, hence preventing prescription error (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2017).
In the diagram, if the medication does not match the patient barcode, then the drugs will be returned and the correct order made. The barcode system can also solve the issue of space because all the data will be stored on the computer hardware. In some situations, data can be stored in a cloudscape. Barcode data processing can also improve the time where the patient can get care. The barcode process can cause various problems in healthcare. One of the issues is that nurses can lose creativity because of the overdependence of electronic systems to perform nursing services (Jimenez, 2017). This problem can be solved by exposing nurses to constant training and education to improve their knowledge and skills.
Conclusion
Barcode data can improve care by reducing time for accessing care, improving quality and safety of care by reducing medical errors, and improve the safety of patient data.
References
Jimenez, M. (2017). Effects of Barcode Medication Administration: Literature Review. Proceedings of the Northeast Business & Economics Association. http://web.a.ebscohost.com/ehost/detail/detail?vid=0&sid=94e40e24-1d39-4b2e-b98e-1f88c6267265%40sdc-v-sessmgr01&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d#AN=134235278&db=bth
McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. (2017). Nursing Informatics and the Foundation of Knowledge (4th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning. ISBN: 978-1284121247.
Samadbeik, M., Shahrokhi, N., Saremian, M., Garavand, A., & Birjandi, M. (2017). Information processing in nursing information systems: An evaluation study from a developing country. Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research, 22(5), 377. doi: 10.4103/ijnmr.IJNMR_201_16
Wilson, N., Jehn, M., Kisana, H., Reimer, D., Meister, D., Valentine, K., … & Clarke, H. (2020). Nurses’ perceptions of implant barcode scanning in surgical services. CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing, 38(3), 131-138. doi: 10.1097/CIN.0000000000000579
Place your order now for a similar assignment and get fast, cheap and best quality work written by our expert level assignment writers. Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
FAQs
[sp_easyaccordion id=”38121″]
BCMA Barcode Medication Administration
In today’s fast-paced healthcare environment, patient safety and efficient care delivery are of utmost importance. One significant advancement that has revolutionized the healthcare industry is the implementation of BCMA, which stands for Barcode Medication Administration. BCMA is a technology-driven process that utilizes barcodes to ensure accurate and secure medication administration. This article delves into the intricacies of BCMA, its benefits, challenges, and its impact on patient care.
Introduction
Medication errors have long been a concern in healthcare settings. These errors can lead to adverse events, patient harm, and even fatalities. To address this issue, healthcare providers are constantly seeking innovative solutions to enhance patient safety and improve medication administration processes. One such solution that has gained significant attention is BCMA, a technology that leverages barcodes to streamline medication administration procedures.
BCMA: Unveiling the Concept
How Barcode Medication Administration Works
BCMA involves a three-step process: verification, documentation, and administration. When a medication is prescribed, a unique barcode is generated and assigned to the medication. This barcode contains essential information such as the medication name, dosage, and patient details. Before administering the medication, the nurse or healthcare provider scans both the patient’s identification wristband and the medication’s barcode. This action ensures that the right patient receives the right medication in the correct dosage and route.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR)
BCMA is seamlessly integrated with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems. This integration allows for real-time documentation of medication administration. The EHR captures the scanned information, providing a comprehensive record of each patient’s medication history. This not only enhances accuracy but also enables healthcare professionals to make informed decisions based on up-to-date patient data.
The Benefits of BCMA
Reducing Medication Errors
One of the primary benefits of BCMA is the substantial reduction in medication errors. By automating the verification process, BCMA minimizes the risk of administering the wrong medication or dosage. This technology acts as a safety net, preventing potentially harmful medication errors and safeguarding patient well-being.
Enhancing Workflow Efficiency
BCMA optimizes workflow efficiency by eliminating manual documentation processes. Nurses can spend more time on direct patient care instead of manual data entry. Additionally, the system alerts healthcare providers to scheduled medication administrations, reducing the chances of missed doses.
Real-time Documentation and Monitoring
The real-time documentation provided by BCMA ensures accurate and up-to-date medication records. This information is vital for continuity of care, enabling seamless transitions between different healthcare providers and settings. Furthermore, real-time monitoring allows prompt intervention in case of adverse reactions or interactions.
Challenges and Solutions
Technological Hurdles and User Adoption
Introducing BCMA may face resistance due to technological challenges and initial unfamiliarity. To overcome this, comprehensive training programs are essential. Healthcare staff should be adequately trained to use the technology effectively, addressing concerns and boosting confidence in its capabilities.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Implementing BCMA may require a shift in established workflows, which can be met with resistance from healthcare professionals. Encouraging open communication, involving staff in the decision-making process, and highlighting the long-term benefits can help overcome this resistance.
Implementing BCMA: Best Practices
Staff Training and Education
Thorough training and education are pivotal for successful BCMA implementation. Hands-on training sessions, user manuals, and continuous support ensure that healthcare professionals are proficient in utilizing the technology.
Integration with Medication Dispensing Systems
Integrating BCMA with automated medication dispensing systems further enhances efficiency. These systems can be programmed to release only the medications that match the scanned barcode, reducing the risk of human error.
BCMA in Action
Case Studies Demonstrating Success
Several healthcare facilities have reported remarkable success after implementing BCMA. Instances of substantial reduction in medication errors and improvements in patient outcomes highlight the positive impact of this technology.
Impact on Patient Care
Increased Patient Safety
BCMA’s accurate medication verification significantly increases patient safety. By ensuring that patients receive the right medications at the right time, the potential for adverse events is significantly reduced.
Improved Healthcare Outcomes
The consistent use of BCMA leads to improved healthcare outcomes. With reduced medication errors, patients experience fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and better overall recovery.
Future Directions of BCMA
Evolving Technology Trends
As technology continues to advance, BCMA is likely to become even more sophisticated. Integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence could further enhance medication administration accuracy and patient safety.
Potential for Artificial Intelligence Integration
The incorporation of AI could enable predictive analysis, identifying patients at a higher risk of adverse reactions. AI-powered systems could also provide real-time alerts for potential drug interactions, enabling swift intervention.
Conclusion
BCMA, the Barcode Medication Administration system, has emerged as a groundbreaking solution for enhancing patient safety and healthcare efficiency. By leveraging barcodes and integrating with electronic health records, BCMA effectively reduces medication errors, streamlines workflows, and improves patient outcomes. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, BCMA stands as a testament to the transformative power of technology in ensuring the well-being of patients.
FAQs
- What is BCMA? BCMA stands for Barcode Medication Administration, a technology that uses barcodes to enhance medication administration accuracy and patient safety.
- How does BCMA work? BCMA involves scanning both the patient’s identification wristband and the medication’s barcode to ensure correct medication administration.
- What are the benefits of BCMA? BCMA reduces medication errors, enhances workflow efficiency, and provides real-time documentation and monitoring.
- How does BCMA impact patient safety? BCMA significantly increases patient safety by preventing medication errors and ensuring accurate administration.
- What is the future of BCMA? BCMA is likely to integrate with advanced technologies like AI, further improving medication administration accuracy and patient outcomes.
The Impact of Barcode Technology on Medication Administration Safety
In the fast-paced world of healthcare, ensuring patient safety is a top priority. One area that has seen significant improvements is medication administration, thanks to the integration of barcode technology. This article delves into the effect of barcode technology on the safety of medication administration, exploring its benefits, challenges, and future potential.
Medication errors are a significant concern in healthcare settings, often leading to adverse patient outcomes. Barcode technology, commonly associated with retail and logistics, has found a crucial role in reducing these errors by enhancing the safety of medication administration.
Understanding Barcode Technology
Barcode technology involves encoding information in a visual pattern of lines and spaces, which can be quickly scanned and interpreted by devices. In healthcare, barcodes are assigned to medication packages and patient wristbands. When scanned, these codes provide a wealth of information, from medication details to patient identification.
Enhancing Medication Administration Safety
Reducing Medication Errors
One of the most significant benefits of barcode technology is its potential to eliminate medication errors. By scanning both the patient’s wristband and the medication packaging, healthcare providers can ensure that the right patient is receiving the right medication, in the right dosage, and at the right time.
Personalized Patient Care
Barcodes allow for a more patient-centric approach. Healthcare providers can access a patient’s medical history, allergies, and other critical information through scanning, ensuring that medication choices are tailored to individual needs.
Efficient Inventory Management
Barcode technology streamlines medication inventory management. Hospitals can easily track medication usage, expiration dates, and restocking needs, leading to better resource utilization and minimizing wastage.
Challenges in Implementation
Initial Costs and Training
Implementing barcode technology requires an initial investment in equipment and software. Moreover, staff need to be trained in using the technology effectively, which can lead to temporary productivity dips during the transition phase.
Technical Glitches
Like any technological system, barcode technology is not immune to technical glitches. A malfunctioning scanner or a misprinted barcode can hinder the smooth workflow and potentially compromise patient safety.
Resistance to Change
Introducing barcode technology often faces resistance from healthcare professionals accustomed to traditional methods. Overcoming this resistance demands a concerted effort in communicating the benefits and providing comprehensive training.
Future Innovations
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
The integration of barcode technology with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) holds immense potential. This seamless combination can provide real-time updates on patient conditions and medication regimens, facilitating better clinical decision-making.
Telemedicine and Remote Medication Dispensing
As telemedicine gains prominence, barcode technology could enable remote medication dispensing. Patients could receive medications at home, with healthcare providers ensuring proper administration through virtual interfaces.
Real-World Success Stories
The Case of Advocate Good Samaritan Hospital
Advocate Good Samaritan Hospital reduced medication errors by over 50% after implementing barcode technology. This success was achieved through increased accuracy in administering medications and improved communication among healthcare teams.
Impact on Pediatric Care at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital
Barcode technology transformed medication safety for pediatric patients at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital. The system ensured precise dosing, reduced adverse events, and empowered parents and caregivers with essential information.
Overcoming Skepticism
Addressing Privacy Concerns
Some skeptics worry about patient data privacy breaches through barcode systems. It’s crucial to establish robust security protocols to safeguard sensitive medical information.
Ensuring Barcode Accuracy
Barcode accuracy is paramount. Regular maintenance of scanning equipment, stringent quality checks on barcode printing, and ongoing staff training are essential to maintaining the system’s integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, barcode technology has revolutionized the safety of medication administration in healthcare settings. By reducing errors, personalizing patient care, and enhancing inventory management, barcodes contribute to better patient outcomes. While challenges like initial costs and technical issues persist, the future promises even more advanced integration and innovative applications of this technology.
FAQs
- How does barcode technology prevent medication errors? Barcode technology prevents medication errors by ensuring the right patient receives the right medication in the right dosage and at the right time through scanning patient wristbands and medication packaging.
- What are some challenges in implementing barcode technology in healthcare? Challenges include initial costs and training, technical glitches, and resistance to change among healthcare professionals.
- Can barcode technology be integrated with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)? Yes, barcode technology can be integrated with EHRs to provide real-time updates on patient conditions and medication regimens.
- Have real-world hospitals benefited from barcode implementation? Yes, hospitals like Advocate Good Samaritan and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital have seen significant reductions in medication errors and improved patient safety through barcode technology.
- How can concerns about patient data privacy with barcode systems be addressed? Concerns about patient data privacy can be addressed by establishing robust security protocols to safeguard sensitive medical information.
What are the steps in barcode medication administration?
Barcode medication administration is a comprehensive process that involves the use of barcode technology to ensure accurate medication administration and patient safety. The process typically includes the following steps:
- Prescription and Order Entry: The process begins with a physician prescribing medication for a patient. This prescription is entered into the electronic health record (EHR) system, which generates an order for the medication.
- Medication Dispensing: The pharmacy receives the medication order and prepares the medication for dispensing. Each medication package is labeled with a unique barcode that contains information about the medication, dosage, and patient details.
- Patient Identification: When the medication is ready to be administered, the healthcare provider verifies the patient’s identity using a barcode wristband worn by the patient. This wristband contains the patient’s unique identification information.
- Medication Verification: Before administering the medication, the healthcare provider scans the barcode on the patient’s wristband and then scans the barcode on the medication packaging. This step ensures that the right medication is being given to the right patient.
- Dosage Confirmation: After scanning the medication barcode, the system displays dosage information. The healthcare provider confirms the dosage accuracy, ensuring that the prescribed dosage matches the administered dosage.
- Real-Time Documentation: Once the medication is administered, the system records the administration time, dosage, and other relevant information in the patient’s electronic health record. This real-time documentation helps in maintaining an accurate medication history.
- Alerts and Allergy Checks: The system may also trigger alerts if there are potential interactions or allergies associated with the medication. This prompts the healthcare provider to reevaluate the medication before administration.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: After administering the medication, the patient’s vital signs and any potential side effects are monitored. This ensures the patient’s well-being and helps detect any adverse reactions promptly.
- Communication and Handoff: In a hospital setting, if the patient is transferred to another department or care provider, barcode technology can assist in ensuring a smooth handoff by providing accurate medication information to the receiving team.
- Reporting and Analysis: Barcode medication administration systems often generate reports and data analytics, which can be used for performance evaluation, identifying trends, and improving the overall medication administration process.
- Training and Maintenance: Healthcare providers and staff receive training on using the barcode technology effectively. Additionally, regular maintenance of barcode scanners and equipment is crucial to ensure the system’s accuracy.
What is the effect of the implementation of barcode technology and an electronic medication administration record on adverse drug events?
The implementation of barcode technology and an electronic medication administration record (eMAR) has had a significant positive effect on reducing adverse drug events (ADEs) in healthcare settings. This powerful combination of technologies enhances patient safety by minimizing medication errors and improving the accuracy of medication administration. Here’s how the integration of barcode technology and eMAR impacts ADEs:
Reduced Medication Errors: Barcode technology ensures that the right medication is administered to the right patient at the right dosage and time. When combined with eMAR, healthcare providers have access to up-to-date and accurate patient medication records. This integration greatly reduces the risk of medication errors, which are a leading cause of ADEs.
Enhanced Patient Identification: Barcode wristbands provide a reliable and foolproof method of patient identification. Coupled with eMAR, this guarantees that medication administration is personalized to each patient. This prevents mix-ups and ensures that patients receive medications intended specifically for them.
Real-Time Allergy Alerts: eMAR systems often include information about patient allergies. When combined with barcode scanning, healthcare providers are instantly alerted if a medication might trigger an allergic reaction. This quick notification helps prevent ADEs related to allergies.
Accurate Dosage Administration: Barcode scanning ensures that the correct dosage is administered. When integrated with eMAR, the system cross-checks the prescribed dosage against the patient’s medical history, minimizing the risk of over- or under-dosage, which can lead to ADEs.
Improved Documentation: eMAR systems automatically document medication administration, creating a comprehensive electronic record. This accurate record allows healthcare teams to monitor medication trends and identify any deviations, enabling early intervention to prevent ADEs.
Real-Time Data Access: Barcode technology and eMAR systems provide healthcare providers with real-time access to patient medication history, drug interactions, and clinical alerts. This information empowers informed decision-making and helps prevent ADEs due to drug-drug interactions.
Streamlined Communication: Barcode technology and eMAR facilitate seamless communication among healthcare teams. Nurses, physicians, and pharmacists can access the same patient data, reducing the likelihood of miscommunication-related ADEs.
Reduced Paper-based Errors: The transition from paper-based medication administration to electronic records reduces errors associated with illegible handwriting and manual documentation. This improves the accuracy of medication administration and reduces ADEs.
Data Analytics for Prevention: Barcode and eMAR systems often generate data analytics that can be used to identify patterns and trends in medication errors. This data-driven approach enables healthcare facilities to proactively address potential ADE risks.
Facilitation of Medication Reconciliation: Barcode technology and eMAR assist in medication reconciliation during care transitions. Accurate and up-to-date medication information helps prevent discrepancies and reduces the risk of ADEs due to inconsistent medication regimens.
In conclusion, the integration of barcode technology and an electronic medication administration record significantly reduces adverse drug events by enhancing patient identification, preventing medication errors, providing real-time alerts, and improving overall communication and documentation. This technological synergy aligns with the healthcare industry’s commitment to patient safety and the reduction of preventable harm.
Ethical issues with barcode medication administration
Barcode medication administration (BCMA) offers numerous benefits in terms of patient safety and medication management, but its implementation can also raise ethical concerns. Here are some of the ethical issues associated with BCMA:
1. Patient Privacy and Data Security: BCMA involves scanning patient identifiers, such as wristbands, which can be viewed as an invasion of privacy. There’s a need to ensure that patient data is stored securely and that only authorized healthcare personnel have access to this information. Protecting patient privacy while utilizing BCMA is a critical ethical consideration.
2. Informed Consent and Autonomy: Patients have the right to be informed about their treatment procedures. Implementing BCMA without adequately explaining its purpose and potential impact on patient care could undermine patient autonomy. Patients should understand how their information is being used and how BCMA can affect their treatment.
3. Technological Dependence and Human Judgment: Overreliance on technology can sometimes lead to complacency in healthcare providers. While BCMA reduces errors, healthcare professionals should not solely rely on the system and must maintain their clinical judgment to ensure optimal patient care.
4. Vulnerability to System Errors: BCMA systems can encounter technical glitches or errors. In such cases, patients might receive incorrect medications due to system failures. Ethical concerns arise when patients are put at risk due to flaws in the technology.
5. Workload and Staff Stress: Implementing BCMA can introduce new workflows and additional responsibilities for healthcare providers. If not managed properly, this can lead to increased stress and fatigue among staff members, potentially compromising patient care.
6. Patient Dignity and Human Interaction: The scanning process may interrupt patient-provider interactions and potentially affect the personal, human touch of healthcare. Maintaining respectful and empathetic interactions while using BCMA is an ethical consideration.
7. Equity and Accessibility: Some patients might not have easily scannable identifiers, such as wristbands, due to various reasons. Ensuring that BCMA does not discriminate against certain patient populations is essential to maintaining ethical standards.
8. Error Responsibility and Accountability: BCMA systems reduce medication errors, but they don’t eliminate them entirely. Determining accountability in cases of error can become complex when both the technology and human factors are involved.
9. Informed Consent for Medication Administration: While BCMA enhances medication safety, it’s important for patients to be informed about the technology’s role in their treatment. This includes explaining how scanning works and how it affects their medication regimen.
10. Training and Competency: Ensuring that healthcare providers are properly trained to use BCMA systems is crucial. Ethical concerns arise if inadequate training leads to errors that could have been prevented with proper education.
11. Medication Reconciliation and Accuracy: BCMA may lead to discrepancies if medication lists are not regularly updated. Ethical considerations include ensuring accurate and up-to-date medication reconciliation to avoid potential harm.
12. Patient Trust and Consent for Data Usage: BCMA generates a significant amount of patient data. It’s important to gain patient consent for the use of this data beyond their immediate treatment, such as for research or quality improvement purposes.
Addressing these ethical concerns involves careful planning, transparent communication with patients, ongoing training for healthcare providers, robust data security measures, and maintaining a balance between technology and human judgment in the healthcare setting.

I am a professional nursing assignment expert offering comprehensive academic support to university nursing students across various institutions. My services are designed to help learners manage their workload effectively while maintaining academic excellence. With years of experience in nursing research, case study writing, and evidence-based reporting, I ensure every paper is original, well-researched, and aligned with current academic standards.
My goal is to provide dependable academic assistance that enables students to focus on practical training and career growth.
Contact me today to receive expert guidance and timely, high-quality nursing assignment help tailored to your academic needs.




