Define what is meant by information. Define what is meant by data. Create two matrices
In this unit, you have learned about management information systems (MIS) and the importance of it. For this assignment, compose a paper that discusses the key differences between data, information, information technology (IT), and information systems (IS). Your paper should address the components listed below.
- Define what is meant by information.
- Define what is meant by data.
- Create two matrices (one for data and one for information) that illustrate the key differences between information and data, place the matrices into your paper, and briefly discuss the differences in one or two paragraphs. Each matrix should contain characteristics and/or facts about the subjects (data and information) that show how they are different.
- Define IT.
- Define IS.
- Using the five-component model as an example, discuss some differences between IT and IS.
Your paper must be a minimum of two pages in length (not counting the title and reference pages), and you must use at least two resources as references. Any information from these resources must be cited and referenced in APA format.
Expert Answer and Explanation
Unit 1 Management
MIS collects data from various systems online, initiates information analysis and thus announces data, in order to help in a policy, build up (Laudon & Laudon, 2012). There are three components of MIS: – Management, Information, and System. These three components aid in building decisions for the managing of the organization.
In regard to the achievements, MIS is a significant aid for improved decision and strategy making. Goals can be quickly achieved by a complete acknowledgment of these elements (Laudon & Laudon, 2012).
Definition of Data and Information
DATA is underdone, a disorderly attribute that requires to be organized. When data is presented in a provided subject to summon its utilization, it is called INFORMATION.
Key-Differences Between Data and Information
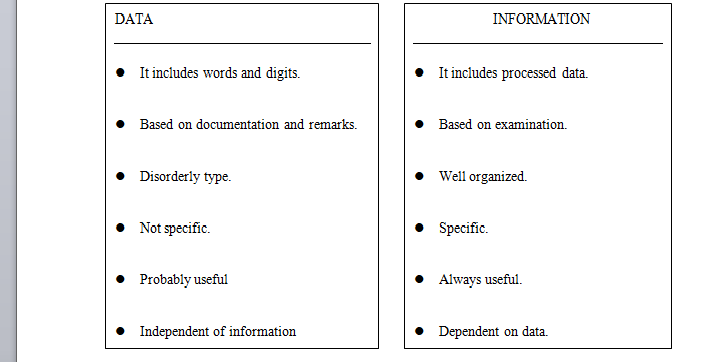
Data are simplified wordings and numerals, whereas information is interpreted data. Similarly, data is preserved in a computer system or just crammed up by an individual while information is more authentic ascompared to data, in addition to this, an exact examination is undergone for the conversion of data into information by the monitor.
Moreover, data are facts that are gathered casually and context that is analyzed, to sum up, the given assets and information is something that ends up providing a significance to the data in a modified manner.
Data may not always be the facet that satisfies the need of the investigator, but information is always specific to the required investigation because every meaningless figure is abolished, during the processing of data. Furthermore, the data collected has a questionable application to the researcher as during its compilation, it does not imply its relevance.
Conversely, information is worthy to him to bring out its particular use. Therefore, data is never contingent on information, in contrast with, information that totally counts on the data provided.
Definition of IT and IS
IT -Information Technology is the use of a computing system to preserve, redeem, transfer, and handle data or information (Davies, 2008).IS -Information Systems is a study of systems with a particular backing to information and the free networks of hardware and software that individuals employ to gather, filter, analyze, develop and also dispense data.
Difference Between It and Is
Based on Five Component Model: -Hardware, software, data, procedures, and people are the five components of an information system; on the analysis of which it is proposed that how these components are brought into service to develop a completely workable system.
IT engages with the technological aspects that aids in the information systems themselves. On the other hand, IS is the arch between the user and the technology. IT is a subdivision of IS.IS is described as an overarching umbrella while IT groups under the IS umbrella.IS concentrates on the given information, whereas IT aids in the collection and the analysis of information.
Therefore, the prime asset is the information here, but IT is dedicated more towards computer software and hardware. IS management is related to the optimization of systems in contrast with IT management that deals with the maintenance of hardware. Apart from this, IS is concerned with the development of IS policy that goes along with vast business aims and claims its specified functions, but IT focuses on framing the necessity to be determined.
Conclusion
Subsequently, for a swift approach towards the attainment of a refined and precise form of data and else to aid the researchers on a particular project of interest, MIS becomes the ultimate idea of productivity. MIS is of great help for the organization that it leaves a great influence on the developer’s performance, roles, and ultimately efficiency MIS provides help in subsequent phases to the managers and thus, in turn, provides great assistance, to come up with a perfectly planned policy.
Alternative Answer
Information Systems Management
Information
Information can be said to be a set of facts that are either earned or provided concerning someone or something. Alternatively, it can also represent processed that that is represented or conveyed by a specific sequence or arrangement (McKinney Jr, & Yoos, 2019).
In retrospect, it can be regarded as the process of resolving uncertainty through the answering of the question, “what is an entity.” The information thus gives meaning to the nature and essence of its characteristics. Depending on the context, information can partake in different meanings related to the notions of communication, education, control, data, understanding, stimuli, perception, and entropy.
Data
Data, also perceived a raw material, is a group of values that contain wither qualitative or quantitative variables concerning a single or multiple objects or individuals. In as much as the terms data and information and more often used interchangeably, the terms possess different meanings in technology, with the most common being data acting the initial raw content before being processed into information (Computer Hope, 2019).
Data can be presented in an unprocessed form such as words, numbers, and symbols that are in relation to events, transactions, and factual interpolations. In its simplest, form data is not very useful and needs to be processed through relations sand grouping in order to be useful and informative.
Differences Between Data and Information
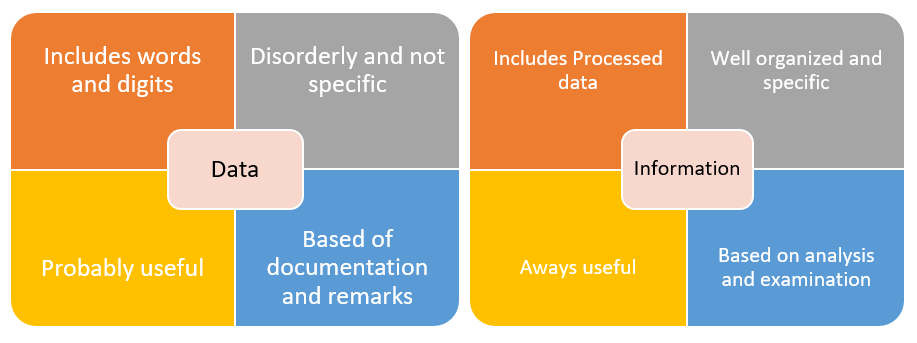
There are four main differences between data and information, as represented in the matrices above. To begin with, while data is comprised of words, digits, and symbols, information is made up of processed data that easily understandable (Computer Hope, 2019). Data is disorderly and not specific to a single entity, information, on the other hand, is well organized and follows a specific order.
Data may or may not be useful, and the probability of usefulness cannot be determined, while information, on the other hand, always contains useful details pertaining to specific concepts (Computer Hope, 2019). The acquisition of data can be from documents or remarks while information is based on the outcome of analysis and examination.
Information Technology
The term information technology refers to the use of computers, networking devices, or other physical devices, processes, and infrastructure to create, store, process, or retrieve different forms of electronic data (Heeks, 2017). Basically, IT contains the hardware, software, network infrastructure, and databases required to implement technological integrations.
Information Systems
Information systems is a broad term for a formal organizational and sociotechnical system designed to collect, store, process, and distribute information (Heeks, 2017). The information system comprises people, systems, and processes that are designed for the manipulation and distribution of the processed data.
Difference Between Information System and Information Technology
The main difference between IS and IT is that IS incorporates both the human resource, technology, and the processes used in dealing with information. Alternatively, information technology is purely technical without human entity in the design and implementation of data within the information system (Ashford, 2018).
The information system is not entirely dependent on technology and computations, while the information system is based on purely technological aspects to provide its functionality. Be that as it may, the two aspects are bridges with the processing of data to form information while they are different in the sense that IT can be a subset of information systems (Ashford, 2018).
As such, information systems can then be applied to bridge the gap between computer processing and human involvement to manipulate the data distributed in the various forms depending on the nature of the output.
References
Ashford. (2018). Information Technology vs. Information Systems: Which Degree is Right for Me?. Ashford University. (2018). Retrieved 2 June 2020, from https://www.ashford.edu/online-degrees/information-technology/information-technology-vs-information-systems-which-degree-is-right-for-me
Computer Hope. (2019). What is the difference between data and information?. Retrieved 2 June 2020, from https://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch001629.htm
Heeks, R. (2017). Information technology, information systems and public sector accountability. In Information Technology in Context: Studies from the Perspective of Developing Countries (pp. 201-219). Routledge.
McKinney Jr, E. H., & Yoos, C. J. (2019). Information as a difference: toward a subjective theory of information. European Journal of Information Systems, 28(4), 355-369.
Place your order now for a similar assignment and get fast, cheap and best quality work written by our expert level assignment writers. Use Coupon Code: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Use Coupon Code: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
FAQs
What is the meaning of data and information?
Data and information are closely related concepts but have distinct meanings:
- Data: Data refers to raw facts, figures, or symbols that represent events, measurements, or conditions. Data are typically unorganized and have little meaning on their own. They could be numbers, words, images, sounds, or any other format. For example, the temperature recorded at different times of the day or the sales figures for a particular product are examples of data.
- Information: Information, on the other hand, is the result of processing, organizing, and interpreting data to make it meaningful and useful. It provides context, relevance, and structure to data, enabling understanding and decision-making. Information answers questions, solves problems, or adds value in some way. For instance, if the temperature data is analyzed to determine trends or patterns, such as identifying the hottest time of day or season, it becomes information.
What are the 10 differences between data and information?
Here are 10 differences between data and information:
- Nature:
- Data: Data are raw, unprocessed facts or figures.
- Information: Information is processed and organized data that has context and meaning.
- Meaning:
- Data: Data lacks context and meaning on its own.
- Information: Information provides context and meaning to data, making it useful for decision-making.
- Form:
- Data: Data can be in various forms such as numbers, text, images, or audio.
- Information: Information is typically presented in a structured format, making it easier to understand and use.
- Purpose:
- Data: Data serves as the foundation for generating information.
- Information: Information is used to answer questions, solve problems, or support decision-making.
- Processing:
- Data: Data undergoes processing to transform it into information.
- Information: Information results from the processing and analysis of data.
- Interpretation:
- Data: Data requires interpretation to extract meaning.
- Information: Information is already interpreted and provides insights or understanding.
- Context:
- Data: Data lacks context and may not be meaningful without additional information.
- Information: Information is contextualized and relevant to a specific context or purpose.
- Actionability:
- Data: Data alone may not be actionable.
- Information: Information is actionable and can guide decisions or actions.
- Volume:
- Data: Data can exist in large volumes.
- Information: Information may be condensed from large volumes of data to highlight key insights.
- Value:
- Data: Data has potential value but requires processing to unlock its value.
- Information: Information has immediate value as it is processed and meaningful.
What is the importance of management information system MIS?
The importance of Management Information Systems (MIS) lies in its ability to provide valuable information to support decision-making, enhance organizational efficiency, and facilitate strategic planning. Here are some key reasons why MIS is important:
- Decision Support: MIS provides timely, accurate, and relevant information to managers and decision-makers, enabling them to make informed decisions. By accessing data and reports generated by MIS, managers can analyze trends, identify opportunities, and address challenges effectively.
- Resource Optimization: MIS helps organizations optimize their resources by providing insights into various aspects of operations, such as inventory management, production schedules, and resource allocation. By having access to real-time data and performance metrics, managers can streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve productivity.
- Performance Monitoring: MIS allows organizations to monitor and evaluate their performance against predefined goals and benchmarks. Managers can track key performance indicators (KPIs) and performance metrics to assess progress, identify areas for improvement, and take corrective actions as needed.
- Strategic Planning: MIS supports strategic planning by providing valuable information about market trends, competitor analysis, and industry insights. With access to this information, organizations can develop strategic plans, set goals, and align their resources and initiatives to achieve long-term success.
- Enhanced Communication: MIS facilitates communication and collaboration within organizations by providing a centralized platform for sharing information and collaborating on projects. By enabling seamless communication and access to shared data, MIS helps improve coordination, teamwork, and decision-making across different departments and levels of the organization.
- Risk Management: MIS helps organizations identify and mitigate risks by providing early warning indicators and risk assessment tools. By monitoring factors such as financial performance, market volatility, and regulatory compliance, MIS enables organizations to anticipate risks, implement risk mitigation strategies, and ensure business continuity.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): MIS supports CRM initiatives by providing insights into customer behavior, preferences, and feedback. By analyzing customer data and interactions, organizations can personalize their marketing efforts, improve customer service, and build stronger relationships with customers.
- Adaptability and Innovation: MIS fosters adaptability and innovation by providing a platform for experimenting with new ideas, technologies, and business models. By leveraging data analytics, machine learning, and other advanced technologies, organizations can identify emerging trends, innovate new products or services, and stay ahead of the competition.
What are the 5 main types of management information systems MIS?
The five main types of Management Information Systems (MIS) are:
- Transaction Processing Systems (TPS):
- TPS are designed to process routine transactions efficiently and accurately. They capture and process data generated by day-to-day business operations such as sales, purchases, inventory management, and payroll processing. TPS provide the foundation for other types of MIS by collecting and organizing raw transaction data.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS):
- DSS help managers and decision-makers analyze data and make informed decisions. They provide tools and techniques for querying data, generating reports, and conducting simulations or “what-if” analysis to evaluate different scenarios. DSS typically incorporate data from various sources and support decision-making at different levels of the organization.
- Executive Information Systems (EIS):
- EIS are specifically designed to support the strategic decision-making needs of top executives. They provide summarized, high-level information from internal and external sources, typically presented in the form of dashboards, charts, and graphs. EIS help executives monitor organizational performance, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and identify strategic opportunities or threats.
- Management Reporting Systems (MRS):
- MRS focus on generating predefined reports and presentations to support managerial decision-making and control. They automate the process of collecting, formatting, and distributing routine reports such as financial statements, budget variance analysis, and operational performance reports. MRS ensure that managers have access to accurate and up-to-date information to monitor progress and make informed decisions.
- Supply Chain Management Systems (SCM):
- SCM systems help organizations manage the flow of goods, services, and information across the entire supply chain, from suppliers to customers. They integrate and automate key supply chain processes such as procurement, production planning, inventory management, logistics, and distribution. SCM systems enable organizations to optimize their supply chain operations, minimize costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.


