Select one organization for this assignment. List and discuss 3 or more efficiencies offered by information technology in that selected setting. Compare and contrast 2 commercially

Signature Assignment Title: Information System Strategic Planning
Signature Assignment Description/Directions: Presentation
Information technology captures, stores, manages, or transmits information related to individuals or the activities of an organization. Information systems include operational and technical systems, administrative systems for managing clients for organizations to improve their efficiency and effectiveness and financial systems for tracking revenue and managing billing systems. The use of information technology is viewed as essential in today’s industry. For this presentation, the learner will:
- Select one organization for this assignment. List and discuss 3 or more efficiencies offered by information technology in that selected setting.
- Compare and contrast 2 commercially available information technology systems available to the selected setting.
- Identify and discuss 5 or more implementation considerations that the organization should consider when adopting an information technology system.
- Explore 2 or more emerging trends in information technology that will influence service delivery in the selected sector.
- List and discuss 3 or more considerations and leaderships’ role in driving technology decision in organizations.
This PowerPoint® (Microsoft Office) or Impress® (Open Office) presentation should be a minimum of 20 slides, including a title, introduction, conclusion and reference slide, with detailed speaker notes and recorded audio comments for all content slides. Use at least four scholarly sources and make certain to review the module’s Signature Assignment Rubric before starting your presentation. This presentation is worth 400 points for quality content and presentation.
Assignment Expectations–
Length: 20 slides; answers must thoroughly address the questions in a clear, concise manner
Structure:
Title slide and reference slides in APA style. (at least 2 slides)
Discuss 3 or more efficiencies offered by information technology in that selected setting: at least 4 slides
Compare and contrast 2 commercially available information technology systems available to the selected setting: at least 2 slides
Identify and discuss 5 or more implementation considerations that the organization should consider when adopting an information technology system: at least 4 slides
Explore 2 or more emerging trends in information technology that will influence service delivery in the selected sector: at least 3 slides
List and discuss 3 or more considerations and leaderships’ role in driving technology decisions in organizations: at least 3 slides
Additionally, because a good presentation has few words on the slides include a script with the verbiage you would say when presenting; script should be a minimum of 50 words per slide.
References: Use the appropriate APA style in-text citations and references for all resources utilized to answer the questions. Include at least three (3) scholarly sources to support your claims.
Format: Save your assignment as a Microsoft PowerPoint document and a Word document (.pptx) and (.doc or .docx) or Open Office Impress.
File name: Name your saved file according to your first initial, last name, and the module number (for example, “RHall Module1.pptx”)
Total Point Value of Signature Assignment: 400 points
M8 Assignment UMBO – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
M8 Assignment PLG – 2, 3, 4, 5, 9
M8 Assignment CLO – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Expert Answer and Explanation

Information system and technology in health care is a strategic component that has significant impact on the efficiency and performance of both clinical and administrative functions in care delivery. This presentation will focus on some of the aspects concerning information technology systems used in health care, implementation considerations and leadership roles in making decisions concerning information technology systems

Information technology systems have changed how health care delivery is conducted, from both the clinical perspective and the administrative function of care delivery. For example, in managed care organizations, health information technology systems can provide the following three efficiencies which will be discussed in detail in the subsequent slides;
- Enhances interprofessional collaboration among care providers within the MCO
- Improves reach and access to care for patients even in remote areas
- Makes administrative functions like billing simpler

Information technology systems can be used to enhance and make interprofessional collaboration easier in MCOs. In an article by Vos et al. (2020), health care technology like EHR can assist health professionals to coordinate patient care on an informed basis at any time and in any place. The same is also true for telehealth and telemedicine services as reported by Johnson and Mahan (2020) where health care professionals are able to communicate with one another using telemedicine.

Health care technology systems can also be used to enhance access to health care services in rural or remote areas where access is low. Using systems such as remote patient monitoring systems, patients within the MCO living in rural or remote areas can get in touch with their care providers at the comfort of their homes (Malasinghe et al., 2019).

Information technology systems also assists in the administrative wing of care delivery. An example can be a function such as billing where IT systems can automate the billing procedure reducing waiting times due to administrative paperwork (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2017). Likewise, keeping an integrated database of patients, which can also be used for follow-up is easier using information technology systems.
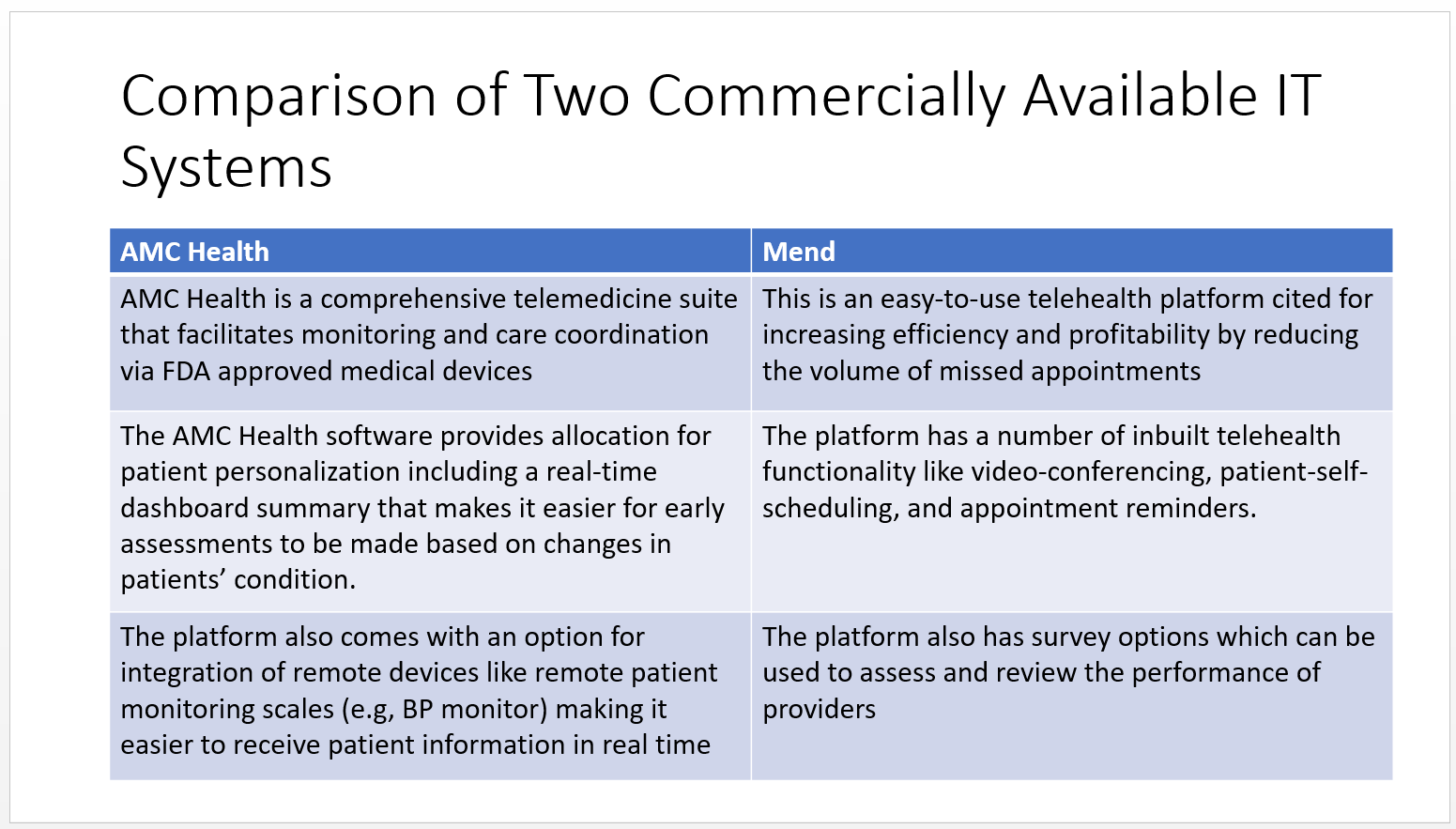
The following is a comparison between two commercial telehealth systems, that is AMC Health and Mend
AMC health
- AMC Health is a comprehensive telemedicine suite that facilitates monitoring and care coordination via FDA approved medical devices
- The AMC Health software provides allocation for patient personalization including a real-time dashboard summary that makes it easier for early assessments to be made based on changes in patients’ condition.
- The platform also comes with an option for integration of remote devices like remote patient monitoring scales (e.g, BP monitor) making it easier to receive patient information in real time
- Mend
- This is an easy-to-use telehealth platform cited for increasing efficiency and profitability by reducing the volume of missed appointments
- The platform has a number of inbuilt telehealth functionality like video-conferencing, patient-self-scheduling, and appointment reminders.
- The platform also has survey options which can be used to assess and review the performance of providers
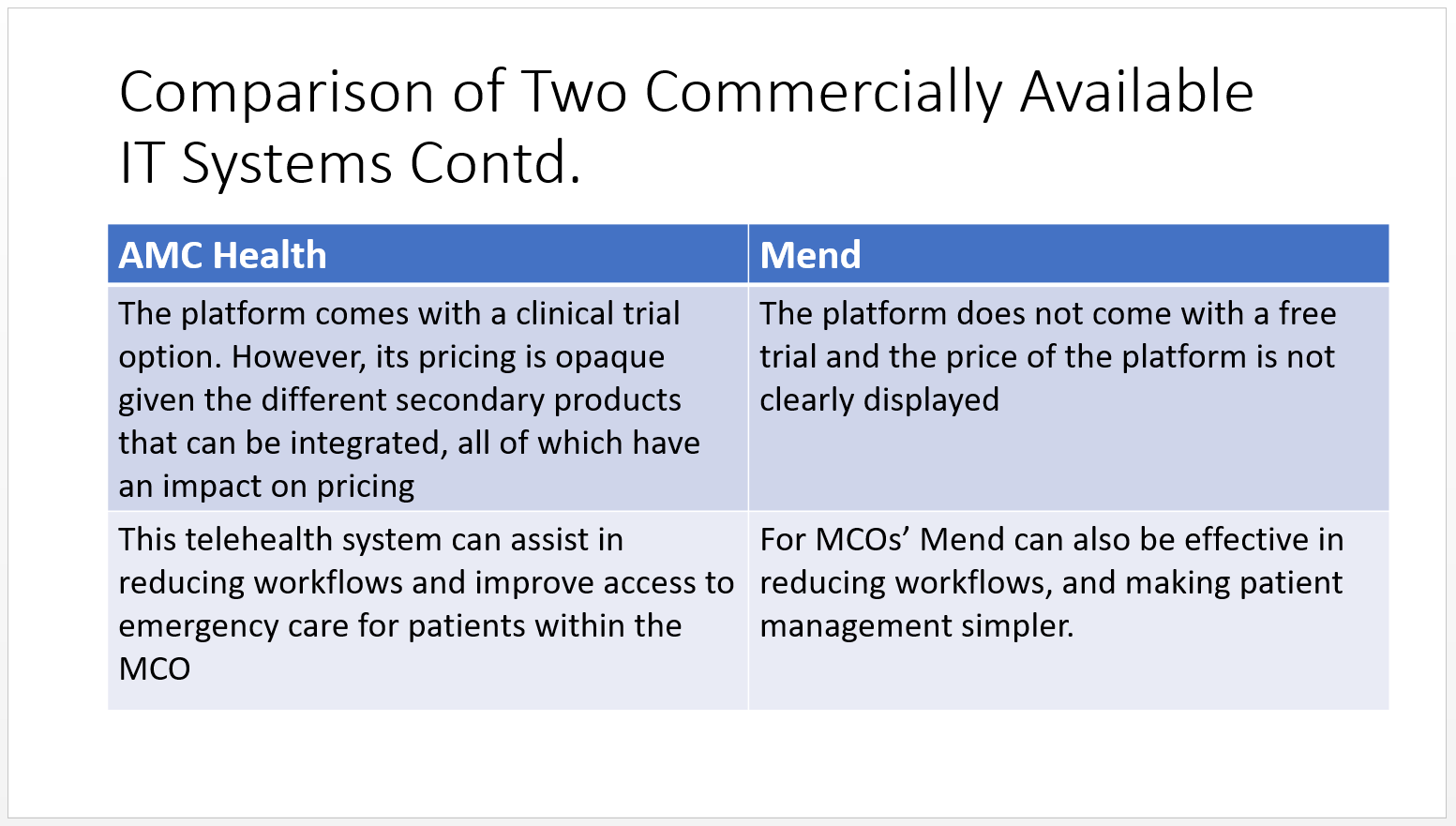
AMC Health
- The platform comes with a clinical trial option. However, its pricing is opaque given the different secondary products that can be integrated, all of which have an impact on pricing
- This telehealth system can assist in reducing workflows and improve access to emergency care for patients within the MCO

There are several considerations to make when implementing health care IT systems. One of the considerations is the skills and competencies possessed by the workforce that will enable them to effectively apply the IT system. The implementation team, including the nurse informaticists need to have the skills and competencies needed to effectively implement the health care IT system.

The organizational culture can either be a facilitator or a barrier to implementation. Therefore, the culture in place should be considered during the implementation stage to ensure that the IT system is successfully implemented. In organizations that already embrace technology, implementing new information systems is much easier compared to those that don’t

Health care information systems are in most cases very costly (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2017). Therefore, they need to be assessed based on the potential benefit they are likely to bring to the organization. In case the intended improvement in workflows for example, does not warrant the cost of purchase, then it will not be meaningful for the organization to implement the system.

Implementation of IT systems come with their own attached ethical and legal considerations. For example, use of health information systems need to conform with the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, and the HIPAA – Health Information Privacy Act. Therefore, implementation needs to ensure that such laws are adhered to prevent ethical and legal issues that might arise.

Another consideration when adopting a health care IT is ease of use. An IT system is supposed to make workflow easier and reduce some of the inefficiencies that characterizes the standard approach to doing things (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2017). Care providers, patients and other stakeholders need to seem improvement in processing time associated with implementation of new systems. Likewise, the new system is supposed to be easy to integrate with other existing systems and also easy to learn how to apply.
With the current CoVID-19 pandemic, there has been an increase telehealth use due to restrictions placed to prevent the spread of infections (Monaghesh & Hajizadeh, 2020). More and more organizations and patients have started appreciating the value and application of telehealth technologies in enhancing patient outcomes. For this reason, the adoption of telehealth systems is expected to increase with more and more stakeholders being exposed to the system.

With increased use of web-based health care applications and systems and management of patients’ data in remote database, health care organizations are likely to increase their investments in cyber security. In a report by Dogaru and Dumitrache, (2017), health care organizations have become the new target for hackers, where they target patient information and use it as ransom. As such to protect patient information, more investments either direct or through subsidiary companies will be channeled towards enhancing cyber security.

Implementation of health care information systems within the organization needs aspects of leadership. The following is a list of some of the leadership considerations, which will be discussed in detail in the subsequent sections of this presentation;
- Effective communication when adopting an IT system within the organization
- Ensuring that the staff have the necessary skillset when implementing an IT system
- Availing the needed resources

In a study by Bardach et al. (2017) one of the issues that was identified by health care workers as being a barrier to effective implementation of telehealth systems was poor communication across disciplines. Therefore, leaders need to ensure that when adopting information systems there is effective communication that will facilitate the implementation or adoption of information system.

Other than communication, it is also the role of the organization’s leadership to ensure that the facility’s staff have the required skillset to adopt the health care IT system (Strudwick et al., 2019). This can be achieved through training or through organization learning where for example, more experienced care providers mentor and pass their knowledge to junior nurses for example. This requires an organizational culture that embrace transformational leadership.

Implementation of technology is a resource intensive venture. It is therefore the role of the leaders to ensure that the needed resources are available to ensure that any decisions made regarding adoption of IT systems can be implemented. Some of the resources that could be considered include human resources (trained personnel), technical resources (computers, internet, etc.,) and financial resources.
Health information systems play an essential role in improving health care delivery. Using health care information systems, a managed care organization can enhance its reach to patients living in remote areas, facilitate communication among care providers in different geographical locations, and also improve workflow. This presentation has provided useful information concerning different aspects involved in the adoption of health care information systems.
Reference
- AMC Health. (n.d.). AMC Health. https://www.amchealth.com/
- Bardach, S. H., Real, K., & Bardach, D. R. (2017). Perspectives of healthcare practitioners: An exploration of interprofessional communication using electronic medical records. Journal of interprofessional care, 31(3), 300–306. https://doi.org/10.1080/13561820.2016.1269312
- Dogaru, D. I., & Dumitrache, I. (2017). Cyber security in healthcare networks. In 2017 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB)(pp. 414-417). IEEE.
- Johnson, K. F., & Mahan, L. B. (2020). Interprofessional Collaboration and Telehealth: Useful Strategies for Family Counselors in Rural and Underserved Areas. The Family Journal, 28(3), 215–224. https://doi.org/10.1177/1066480720934378
- Malasinghe, L. P., Ramzan, N., & Dahal, K. (2019). Remote patient monitoring: a comprehensive study. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 10(1), 57-76.
- Mend (n.d.). Mend. https://www.mend.com/
- Monaghesh, E., & Hajizadeh, A. (2020). The role of telehealth during COVID-19 outbreak: a systematic review based on current evidence. BMC public health, 20(1), 1193. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09301-4
- McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. (2017). Nursing Informatics and the Foundation of Knowledge(4th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning. ISBN: 978-1284121247
- Strudwick, G., Booth, R. G., Bjarnadottir, R. I., Rossetti, S. C., Friesen, M., Sequeira, L., & Srivastava, R. (2019). The role of nurse managers in the adoption of health information technology: findings from a qualitative study. JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration, 49(11), 549-555. doi: 10.1097/NNA.0000000000000810
- Vos, J. F., Boonstra, A., Kooistra, A., Seelen, M., & van Offenbeek, M. (2020). The influence of electronic health record use on collaboration among medical specialties. BMC health services research, 20(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05542-6
Place your order now for a similar assignment and get fast, cheap and best quality work written by our expert level assignment writers. Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order

Answered Questions:
ANSWERED!! Assume you are a nurse manager on a unit
ANSWERED!! Watch the Diary of Medical Mission Trip
ANSWERED!! Re-read Take a Closer Look: Exploring Claude
ANSWERED!! Develop and submit a personal leadership
ANSWERED!! Develop and submit a personal leadership
ANSWERED!! Mrs. Adams a 68-year-old widow who was
what are 3 types of clinical information systems, types of healthcare information systems, types of health information systems pdf
hospital information system examples, health information system pdf, 2 types of health information, advantages of health information system, components of health information system
which would be the best revision for this opening sentence of a sales message, persuasion is necessary when, many clever sales messages combine in the interest section of the message
while writing a persuasive message you need information about your, which of the following can make persuasion effective, how should elan structure her message to her boss about the refrigerator check all that apply, which guidelines should you follow for a professional blog choose every correct answer
What Are 3 Types of Clinical Information Systems?
I. Introduction
In today’s rapidly advancing healthcare landscape, the effective management and utilization of clinical information have become essential. Clinical information systems play a pivotal role in capturing, storing, and disseminating patient data, thereby enabling healthcare providers to deliver high-quality care. This article explores the three main types of clinical information systems, their benefits, challenges, and impact on healthcare.
II. Clinical Information Systems
Clinical information systems encompass a range of digital solutions designed to facilitate the storage, retrieval, and analysis of patient data. These systems leverage technology to enhance healthcare delivery, decision-making, and patient outcomes.
A. Definition and Overview
Clinical information systems refer to the integration of electronic health records (EHRs), computerized physician order entry (CPOE), and clinical decision support systems (CDSS). These systems serve as a comprehensive platform for healthcare professionals to access and manage patient information efficiently.
B. Importance of Clinical Information Systems
Clinical information systems are vital for promoting patient safety, improving care coordination, and enhancing clinical outcomes. By enabling seamless information sharing among healthcare providers, these systems streamline workflows and reduce errors, ultimately leading to better patient care.
III. Types of Clinical Information Systems
There are three primary types of clinical information systems: Electronic Health Records (EHRs), Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE), and Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS). Each system serves a unique purpose in healthcare delivery.
A. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
1. Benefits and Features
CPOE systems enable healthcare providers to electronically enter and manage patient orders for medications, tests, and procedures. The key benefits of CPOE include:
- Reduction in medication errors and adverse events
- Improved accuracy and legibility of orders
- Integration with decision support tools for clinical guidance
- Efficient transmission of orders to relevant departments
2. Challenges and Limitations
CPOE systems also encounter challenges, such as:
- Resistance to change and workflow disruption during implementation
- Learning curve for healthcare professionals transitioning to electronic order entry
- Alert fatigue due to excessive notifications
C. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
1. Benefits and Features
CDSS utilize advanced algorithms and medical knowledge databases to assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions. The key benefits of CDSS include:
- Real-time alerts and reminders for critical information
- Clinical guidelines and best practices integration
- Improved diagnosis accuracy and treatment selection
- Support for evidence-based medicine and research
2. Challenges and Limitations
CDSS face challenges, including:
- Integration with existing systems and workflows
- Overreliance on system recommendations without proper clinical judgment
- Information overload leading to reduced usability
IV. Integration and Interoperability
To achieve the full potential of clinical information systems, integration and interoperability are crucial. Interconnectivity among various systems allows for seamless data sharing, while standardization and data exchange protocols enable efficient communication between different healthcare providers and organizations.
V. Impact on Healthcare
Clinical information systems have a profound impact on healthcare delivery, with benefits ranging from improved patient care and safety to enhanced efficiency and research capabilities.
A. Improved Patient Care and Safety
By providing healthcare professionals with instant access to accurate and comprehensive patient information, clinical information systems contribute to improved diagnosis, treatment, and care coordination. They also help reduce medical errors, adverse events, and medication-related issues.
1. Benefits and Features
EHRs are comprehensive digital records that contain a patient’s medical history, diagnoses, treatments, medications, and other pertinent information. The key benefits of EHRs include:
- Enhanced accessibility and availability of patient data
- Improved care coordination and communication among healthcare providers
- Efficient management of patient records and documentation
- Support for clinical decision-making through real-time data access
2. Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, EHRs also face challenges, such as:
- Implementation and adoption hurdles
- Privacy and security concerns
- Interoperability issues among different EHR systems
B. Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE)
1. Benefits and Features
CPOE systems enable healthcare providers to electronically enter and manage patient orders for medications, tests, and procedures. The key benefits of CPOE include:
- Reduction in medication errors and adverse events
- Improved accuracy and legibility of orders
- Integration with decision support tools for clinical guidance
- Efficient transmission of orders to relevant departments
2. Challenges and Limitations
CPOE systems also encounter challenges, such as:
- Resistance to change and workflow disruption during implementation
- Learning curve for healthcare professionals transitioning to electronic order entry
- Alert fatigue due to excessive notifications
C. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
1. Benefits and Features
CDSS utilize advanced algorithms and medical knowledge databases to assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions. The key benefits of CDSS include:
- Real-time alerts and reminders for critical information
- Clinical guidelines and best practices integration
- Improved diagnosis accuracy and treatment selection
- Support for evidence-based medicine and research
2. Challenges and Limitations
CDSS face challenges, including:
- Integration with existing systems and workflows
- Overreliance on system recommendations without proper clinical judgment
- Information overload leading to reduced usability
IV. Integration and Interoperability
To achieve the full potential of clinical information systems, integration and interoperability are crucial. Interconnectivity among various systems allows for seamless data sharing, while standardization and data exchange protocols enable efficient communication between different healthcare providers and organizations.
V. Impact on Healthcare
Clinical information systems have a profound impact on healthcare delivery, with benefits ranging from improved patient care and safety to enhanced efficiency and research capabilities.
A. Improved Patient Care and Safety
By providing healthcare professionals with instant access to accurate and comprehensive patient information, clinical information systems contribute to improved diagnosis, treatment, and care coordination. They also help reduce medical errors, adverse events, and medication-related issues.
B. Enhanced Efficiency and Workflow
Clinical information systems streamline administrative tasks, such as documentation, billing, and scheduling, enabling healthcare providers to focus more on patient care. These systems also automate routine processes, reducing the time spent on manual tasks and facilitating efficient workflows.
C. Research and Population Health Management
Clinical information systems offer valuable data for research purposes and population health management. Aggregated patient data allows for population-level analysis, identification of trends, and assessment of healthcare interventions’ effectiveness. This information aids in evidence-based decision-making and the development of personalized treatment plans.
VI. Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to evolve, clinical information systems will witness further advancements. Emerging trends include the adoption of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics to improve clinical outcomes, enhance precision medicine, and enable proactive patient care.
VII. Conclusion
Clinical information systems, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs), Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE), and Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS), are integral to modern healthcare. These systems streamline data management, facilitate informed decision-making, and contribute to improved patient outcomes. With ongoing developments and innovations, clinical information systems will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare.
VIII. FAQs
Q1. Are clinical information systems only used in hospitals?
No, clinical information systems are utilized in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and other care facilities. They are designed to support healthcare professionals in delivering efficient and effective care.
Q2. Can clinical information systems be accessed remotely?
Yes, with the advancements in technology and the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions, many clinical information systems can be accessed remotely, allowing healthcare providers to review patient data from anywhere with an internet connection.
Q3. Do clinical information systems replace the need for paper records?
Clinical information systems aim to digitize and streamline patient data, reducing reliance on paper records. However, in some cases, a hybrid approach combining electronic and paper records may still be used, especially during the transition phase.
Q4. How do clinical information systems ensure patient privacy and data security?
Clinical information systems employ robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular audits, to safeguard patient privacy and protect sensitive health information from unauthorized access or breaches.
Q5. Are there any downsides to implementing clinical information systems?
While clinical information systems offer numerous benefits, their implementation can be challenging and require significant investment of time, resources, and training. It is essential to address potential challenges such as system integration, user adoption, and data standardization to ensure a successful implementation.
Advantages of Health Information Systems
Health Information Systems (HIS) play a crucial role in modern healthcare by utilizing technology to manage, store, and exchange patient information. These systems offer several significant advantages that contribute to improved patient care, streamlined workflows, and enhanced decision-making. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of Health Information Systems:
- Efficient Data Management: Health Information Systems enable healthcare providers to store, organize, and manage patient data in a structured and accessible manner. This digital approach eliminates the need for cumbersome paper-based records and allows for quick and efficient retrieval of patient information, saving time and reducing errors.
- Enhanced Care Coordination: HIS promotes seamless communication and collaboration among healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care. By having a centralized repository of patient data, different healthcare professionals can access relevant information, such as medical history, test results, and treatment plans. This improves care coordination, reduces duplication of tests, and ensures continuity of care.
- Improved Patient Safety: HIS contributes to patient safety by reducing medical errors and adverse events. With electronic systems, healthcare providers can easily track and monitor medication orders, allergies, and potential drug interactions, thus minimizing medication errors. Decision support tools integrated within HIS provide real-time alerts and reminders for critical information, ensuring safer and more accurate patient care.
- Efficient Workflow and Productivity: Health Information Systems automate administrative tasks, such as appointment scheduling, billing, and documentation. By streamlining these processes, healthcare professionals can focus more on patient care, leading to increased productivity and improved workflow efficiency. Automated reminders and notifications help prevent missed appointments and support timely interventions.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: HIS allows for comprehensive data analysis and reporting, providing valuable insights for healthcare management and decision-making. By aggregating patient data, HIS enables the identification of trends, monitoring of health outcomes, and assessment of quality indicators. This data-driven approach supports evidence-based practice, research, and population health management.
- Improved Accessibility and Portability: With Health Information Systems, patient data becomes easily accessible to authorized healthcare providers, regardless of their location. This enables remote consultations, telemedicine services, and efficient sharing of information between different healthcare organizations. The portability of electronic health records ensures continuity of care when patients visit different healthcare facilities or specialists.
How Does Information Technology Improve the Flow of Communication Between Members of the Healthcare Team?
Effective communication is crucial in any healthcare setting as it directly impacts patient outcomes and the overall quality of care provided. The ability of healthcare professionals to communicate efficiently and accurately is essential for proper diagnosis, treatment, and patient management. In recent years, information technology (IT) has played a pivotal role in improving the flow of communication between members of the healthcare team. By leveraging advanced tools and technologies, healthcare professionals can now collaborate seamlessly, exchange critical information, and make well-informed decisions. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which information technology enhances communication within the healthcare team.
Importance of Effective Communication in Healthcare
Before delving into the benefits of information technology, let’s first understand why effective communication is paramount in healthcare. In a healthcare environment, multiple stakeholders, including physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and other allied healthcare professionals, work together to deliver comprehensive care to patients. Clear and accurate communication is essential to ensure that everyone is on the same page, facilitating efficient care coordination and patient safety. Effective communication also helps in preventing medical errors, reducing readmission rates, and improving patient satisfaction.
Challenges in Communication Within the Healthcare Team
While the importance of communication is widely recognized in healthcare, several challenges often impede its effectiveness. These challenges can range from language barriers to geographical constraints and hierarchical structures within healthcare organizations.
Language Barriers
In multicultural healthcare settings, language barriers can pose significant challenges to effective communication. When healthcare professionals and patients do not share a common language, it can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and errors in diagnosis and treatment. Information technology can help overcome these language barriers by providing translation services, language interpretation tools, and multilingual communication platforms.
Geographical Barriers
In large healthcare organizations or those with multiple locations, communication between team members across different physical sites can be challenging. Geographical barriers hinder quick and direct communication, resulting in delays, miscommunication, and potential patient harm. Information technology offers solutions such as secure messaging apps, video conferencing, and telehealth services, enabling real-time communication regardless of physical location.
Hierarchical Barriers
The hierarchical structure within healthcare organizations can sometimes impede effective communication. Nurses may hesitate to communicate their concerns to physicians, and junior staff may feel intimidated by senior colleagues. Information technology can create a more level playing field by providing platforms that encourage open and transparent communication. Communication tools that allow for instant messaging, discussion forums, and collaborative document sharing can break down hierarchical barriers and facilitate effective teamwork.
Information Technology Solutions for Communication
Information technology provides a wide range of solutions to improve communication within the healthcare team. Let’s explore some of the key IT tools and technologies that are transforming healthcare communication.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Electronic health records have revolutionized the way patient information is stored, accessed, and shared. EHRs provide a centralized platform for healthcare professionals to view comprehensive patient data, including medical history, laboratory results, medication records, and imaging reports. By having access to real-time patient information, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions and communicate effectively, ensuring continuity of care.
Communication Platforms and Messaging Apps
Dedicated communication platforms and messaging apps designed for healthcare facilitate secure and efficient communication between team members. These platforms offer features such as instant messaging, voice and video calls, file sharing, and task management. By using such platforms, healthcare professionals can communicate in real-time, share critical information, and collaborate seamlessly, enhancing overall efficiency and patient safety.
Telehealth and Teleconferencing
Telehealth has emerged as a game-changer in healthcare communication, especially in remote or underserved areas. Telehealth allows healthcare professionals to provide virtual consultations, monitor patients remotely, and facilitate follow-up care. Teleconferencing enables multidisciplinary discussions and consultations among healthcare team members, regardless of their physical location. These technologies improve access to care, minimize travel requirements, and enable efficient communication and collaboration.
Benefits of Information Technology in Healthcare Communication
The integration of information technology in healthcare communication yields numerous benefits for both healthcare professionals and patients.
Improved Coordination and Collaboration
Information technology streamlines communication processes, enabling healthcare professionals to collaborate more effectively. Through shared platforms and real-time updates, team members can coordinate their efforts, assign tasks, and exchange information efficiently. This results in improved care coordination, reduced errors, and enhanced patient outcomes.
Enhanced Accessibility to Patient Information
With the digitization of patient records, healthcare professionals can access patient information anytime and anywhere. Information technology eliminates the need for paper-based records and allows for quick retrieval of patient data, including medical histories, medication lists, and test results. This accessibility facilitates informed decision-making and accurate communication among team members.
Real-time Communication
Information technology tools facilitate real-time communication, which is essential in critical situations. Healthcare professionals can exchange messages, share updates, and seek immediate input from colleagues when faced with urgent patient care needs. Real-time communication improves response times, expedites decision-making, and enhances patient safety.
Streamlined Workflows
By integrating communication tools into existing workflows, information technology streamlines processes and reduces administrative burden. For example, appointment scheduling systems and automated reminders help optimize appointment management, reducing the likelihood of missed appointments and improving patient engagement. Streamlined workflows improve efficiency, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
Security and Privacy Considerations
While the benefits of information technology in healthcare communication are immense, it is essential to address security and privacy concerns. Protecting patient information is of paramount importance to maintain confidentiality and comply with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
HIPAA Compliance
Healthcare organizations must ensure that the information technology solutions they implement comply with HIPAA regulations. This involves robust security measures, including access controls, encryption, and regular audits. HIPAA compliance ensures that patient data remains secure and protected from unauthorized access.
Encryption and Secure Networks
Communication platforms and networks should employ encryption techniques to safeguard sensitive patient information during transmission. Encryption converts data into a format that is unreadable without the decryption key, preventing unauthorized interception or access. Secure networks further strengthen the protection of patient data by implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures.
Data Integrity and Confidentiality
Healthcare organizations must maintain data integrity and confidentiality when using information technology for communication. This includes measures such as regular data backups, access controls, and strict user authentication protocols. By ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of patient data, healthcare professionals can communicate with confidence, knowing that the information shared remains accurate and protected.
Success Stories and Case Studies
Several healthcare organizations have successfully implemented information technology solutions to improve communication within their teams. Case studies and success stories highlight the positive impact of technology on healthcare communication, demonstrating improved patient outcomes, reduced errors, and enhanced collaboration.
One notable success story is the implementation of a secure messaging app in a large hospital system. The app allowed healthcare professionals to communicate directly, eliminating the need for time-consuming phone calls or pager messages. The app’s features, such as message read receipts and priority tagging, improved response times and enabled efficient communication, especially in critical situations. The hospital system reported a significant reduction in communication errors, improved care coordination, and enhanced patient satisfaction.
Future Trends and Advancements
As technology continues to evolve, so does its impact on healthcare communication. Future trends and advancements in information technology will further enhance communication between members of the healthcare team.
One prominent trend is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms in healthcare communication. AI-powered chatbots can provide automated responses, schedule appointments, and answer frequently asked questions, freeing up healthcare professionals’ time for more complex tasks. Machine learning algorithms can analyze communication patterns, identify areas for improvement, and provide personalized recommendations to enhance communication effectiveness.
Another advancement is the integration of wearable devices and sensors into healthcare communication. These devices can collect real-time data on patient vital signs, activity levels, and sleep patterns, enabling healthcare professionals to monitor patients remotely and intervene when necessary. Wearable devices also facilitate seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers, allowing for continuous feedback and support.
Conclusion
Information technology has transformed healthcare communication, improving the flow of information between members of the healthcare team. By leveraging advanced tools and technologies, healthcare professionals can overcome challenges such as language barriers, geographical constraints, and hierarchical structures. Information technology solutions, including electronic health records, communication platforms, and telehealth services, enhance collaboration, streamline workflows, and facilitate real-time communication. However, it is crucial to prioritize security and privacy to protect patient information. Future advancements in AI, machine learning, and wearable technology will further revolutionize healthcare communication, ultimately benefiting patient care and outcomes.
FAQs
Q1. How does information technology improve patient safety in healthcare communication?
Information technology improves patient safety by enabling accurate and timely communication among healthcare team members. It allows for quick access to patient information, enhances care coordination, and reduces the likelihood of errors or omissions in communication.
Q2. What are the security measures in place to protect patient data in healthcare communication?
Security measures include HIPAA compliance, encryption during data transmission, secure networks, access controls, and regular data backups. These measures ensure that patient data remains confidential, protected, and only accessible to authorized individuals.
Q3. Can information technology solutions help overcome language barriers in healthcare communication?
Yes, information technology solutions can help overcome language barriers through translation services, language interpretation tools, and multilingual communication platforms. These tools facilitate effective communication between healthcare professionals and patients who do not share a common language.
Q4. How does telehealth improve communication in healthcare?
Telehealth enables virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and multidisciplinary discussions among healthcare team members. It eliminates geographical barriers, allows for real-time communication, and enhances access to care, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
Q5. What are the future trends in healthcare communication?
Future trends in healthcare communication include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms for automated responses and personalized recommendations. Additionally, wearable devices and sensors will play a significant role in remote monitoring and continuous communication between patients and healthcare providers.

I am a professional nursing assignment expert offering comprehensive academic support to university nursing students across various institutions. My services are designed to help learners manage their workload effectively while maintaining academic excellence. With years of experience in nursing research, case study writing, and evidence-based reporting, I ensure every paper is original, well-researched, and aligned with current academic standards.
My goal is to provide dependable academic assistance that enables students to focus on practical training and career growth.
Contact me today to receive expert guidance and timely, high-quality nursing assignment help tailored to your academic needs.

