Last updated on August 27th, 2025 at 06:59 am
Table of Contents
ToggleAs an advanced registered nurse, you will serve as a leader within your organization
As an advanced registered nurse, you will serve as a leader within your organization. Part of this role will entail being a change agent and spurring positive change on behalf of patients, colleagues, and the industry.
Consider a situation you experienced previously where change did not go as planned in your health care organization.
Create a 10-15-slide PowerPoint presentation in which you assess the situation and provide the steps that should have been taken to successfully implement change.
Create speaker notes of 100-250 words for each slide.
For the presentation of your PowerPoint, use Zoom to create a video presentation. Refer to the Topic 3 Resources for additional guidance on recording your presentation with Zoom. Include additional slides for the title and Zoom link at the beginning and for References at the end.
Include the following in your presentation:
- Describe the background of the situation and the rationale for and goal(s) of the change. Consider the ethical, social, legal, economic, and political implications of practice change in your response.
- Outline the advanced registered nurse’s role as change agent within the interprofessional and dynamic health care environment.
- Identify the key interprofessional stakeholders (both internal and external) that should be involved in change efforts.
- Discuss an appropriate change theory or model that could be used to achieve results. Explain why the theory or model selected is best for the situation. Include the ethical, social, legal, economic, and political implications of applying the change management strategies to practice change in your response.
- As an advanced registered nurse, outline how you would initiate the change.
- Describe the impact to the organization if the change initiative is unsuccessful again, and potential steps the interprofessional team could take if the change is unsuccessful.
- Predict what additional factors will drive upcoming organizational change for the organization and outline the advanced registered nurse’s role as change agent.
You are required to cite three to five sources to complete this assignment. Sources must be published within the past 5 years and appropriate for the assignment criteria and nursing content.
Refer to the resource, “Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations,” located in the Student Success Center, for additional guidance on completing this assignment in the appropriate style.
While APA style is not required for the body of this assignment, solid academic writing is expected, and documentation of sources should be presented using APA formatting guidelines, which can be found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. A link to the LopesWrite technical support articles is located in Class Resources if you need assistance.
Expert Answer
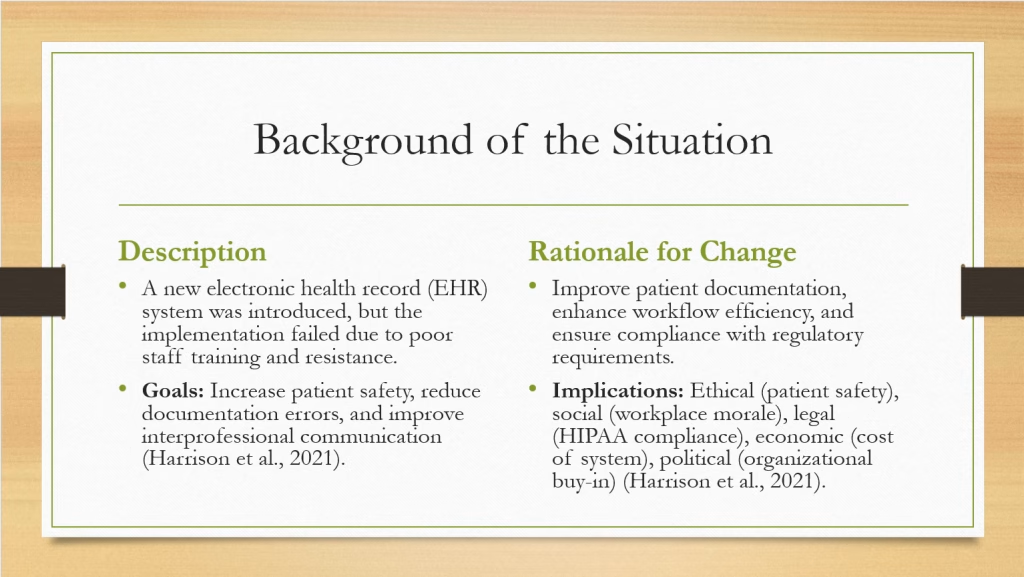
The situation I encountered involved the implementation of a new electronic health record (EHR) system in a busy hospital setting. The goal of this change was to streamline documentation, enhance interdisciplinary communication, and improve patient safety by reducing medication errors and improving access to patient histories (Harrison et al., 2021). However, the initiative was unsuccessful due to several key issues, including inadequate staff training, resistance from providers who were accustomed to the previous system, and technical glitches that led to workflow disruptions.
Additionally, there was poor communication regarding the transition process, which resulted in frustration among healthcare staff and decreased efficiency in patient care. This failure had significant ethical implications, as delayed documentation impacted patient safety. Socially, staff morale declined due to the increased workload.

Advanced registered nurses play a crucial role in leading change by advocating for evidence-based practices, guiding staff, and addressing resistance. As change agents, they collaborate with interprofessional teams to ensure patient-centered improvements while considering ethical and organizational impacts.

Successful change requires engaging internal and external stakeholders. Internal stakeholders include nurses, physicians, and administrative leaders, while external stakeholders may include policymakers, patients, and insurance providers. Identifying and involving these groups early fosters cooperation and shared accountability.

Lewin’s Change Management Model is effective for structured implementation. It consists of three phases: unfreezing (preparing for change), changing (implementing the plan), and refreezing (ensuring long-term adoption). This model provides clear guidance for addressing resistance and sustaining improvements.

Change initiatives must comply with ethical and legal standards while considering social and economic implications. Ensuring patient safety, maintaining financial feasibility, and aligning with healthcare policies are critical to a smooth transition.

To successfully implement change, an advanced registered nurse should assess readiness, communicate the vision, engage stakeholders, provide training, and evaluate progress. Using evidence-based approaches and fostering teamwork will enhance the success of the initiative.

Upcoming changes in healthcare will be influenced by technology, policy updates, and evolving patient needs. Nurses must stay proactive, advocate for improvements, and lead transformations that align with evidence-based best practices.

Upcoming changes in healthcare will be influenced by technology, policy updates, and evolving patient needs. Nurses must stay proactive, advocate for improvements, and lead transformations that align with evidence-based best practices.

Advanced registered nurses will play an increasing role in driving change by using leadership skills, participating in policy discussions, and promoting interdisciplinary collaboration to enhance patient care and system efficiency.

Change in healthcare is inevitable, but its success depends on strategic planning, strong leadership, and interprofessional collaboration. By applying structured models and fostering teamwork, advanced practice nurses can ensure successful transformations that benefit both patients and organizations.
References
Basinska, K., Wellens, N. I., Simon, M., Zeller, A., Kressig, R. W., & Zúñiga, F. (2021). Registered nurses in expanded roles improve care in nursing homes: Swiss perspective based on the modified Delphi method. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 77(2), 742-754. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.14644
Cheraghi, R., Ebrahimi, H., Kheibar, N., & Sahebihagh, M. H. (2023). Reasons for resistance to change in nursing: an integrative review. BMC nursing, 22(1), 310. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-023-01460-0
Harrison, R., Fischer, S., Walpola, R. L., Chauhan, A., Babalola, T., Mears, S., & Le-Dao, H. (2021). Where do models for change management, improvement and implementation meet? A systematic review of the applications of change management models in healthcare. Journal of healthcare leadership, 85-108. https://doi.org/10.2147/JHL.S289176
Memon, F. A. (2021). Improving employee’s engagement in change: Reassessing Kurt Lewin’s model. City University Research Journal, 11(1). http://www.cusitjournals.com/index.php/CURJ/article/view/282
Place your order now for a similar assignment and get fast, cheap and best quality work written by our expert level assignment writers. Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order

Advanced Practice Nursing Leadership: Driving Organizational Change as Healthcare Change Agents
Advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) have evolved beyond traditional bedside care to become pivotal leaders and change agents within healthcare organizations. Creating a future in which opportunities to optimize health are more equitable will require disrupting the deeply entrenched prevailing paradigms of health care, which in turn will require enlightened, diverse, courageous, and competent leadership. This comprehensive guide explores how advanced registered nurses serve as transformative leaders, drive positive change, and collaborate with interprofessional stakeholders to improve patient outcomes and organizational effectiveness.
Understanding the Advanced Practice Nurse Leadership Role
Defining Advanced Practice Registered Nurses
Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs) include nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, nurse anesthetists, and nurse midwives. APRNs are often primary care providers and are at the forefront of providing preventive care services to the public. These highly educated professionals possess specialized knowledge, skills, and competencies that position them uniquely to lead healthcare transformation initiatives.
The Evolution of Nursing Leadership
The nursing profession has undergone significant transformation over the past decades, with advanced practice nurses assuming increasingly complex leadership roles. Develops leadership in and integrates the role of the nurse practitioner within the healthcare system · Employs consultative and leadership skills with intraprofessional and interprofessional teams to create change in health care and within complex healthcare delivery systems
Core Leadership Competencies for Advanced Practice Nurses
Strategic Vision and Planning
Advanced practice nurses must develop and articulate a clear vision for healthcare improvement. This involves:
- Analyzing current healthcare trends and challenges
- Identifying opportunities for innovation and improvement
- Developing strategic plans that align with organizational goals
- Communicating vision effectively to diverse stakeholders
Change Management Expertise
The NPD practitioner serves as a change agent within the interprofessional practice and learning environment, whereas the specialist leads change initiatives. Effective change management requires:
Table 1: Essential Change Management Skills for Advanced Practice Nurses
| Competency Area | Key Skills | Impact on Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Assessment | Environmental scanning, stakeholder analysis, readiness evaluation | Informed decision-making |
| Planning | Strategic planning, resource allocation, timeline development | Structured implementation |
| Implementation | Project management, communication, training coordination | Successful change adoption |
| Evaluation | Outcome measurement, continuous improvement, sustainability planning | Long-term success |
Clinical Excellence and Evidence-Based Practice
Advanced practice nurses must maintain clinical expertise while leading organizational initiatives. This dual focus ensures that change efforts are grounded in best practices and clinical evidence.
The Change Agent Role in Healthcare Organizations
Understanding Organizational Change
Healthcare organizations face constant pressure to adapt to evolving regulations, technologies, and patient needs. Advanced practice nurses serve as catalysts for positive change by:
- Identifying inefficiencies and improvement opportunities
- Championing evidence-based interventions
- Facilitating smooth transitions during organizational changes
- Measuring and reporting outcomes
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Change resistance is natural in healthcare settings where patient safety is paramount. Successful nurse leaders employ strategies to address resistance:
Table 2: Common Sources of Change Resistance and Mitigation Strategies
| Resistance Source | Manifestation | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Fear of Unknown | Anxiety about new procedures | Education and transparent communication |
| Resource Constraints | Concerns about workload increases | Adequate training and support |
| Past Failures | Skepticism based on previous experiences | Small wins and incremental progress |
| Cultural Barriers | “We’ve always done it this way” mentality | Cultural assessment and targeted interventions |
Interprofessional Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement
The Importance of Interprofessional Collaboration
Improved health care collaboration … care has been shown to improve patient outcomes such as reducing preventable adverse drug reactions, decreasing morbidity and mortality rates and optimizing medication dosages. Teamwork has also been shown to provide benefits to health
Key Interprofessional Stakeholders
Advanced practice nurses must collaborate with diverse stakeholders to drive organizational change effectively:
Table 3: Key Stakeholders in Healthcare Change Initiatives
| Stakeholder Group | Role in Change Process | Collaboration Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Physicians | Clinical decision-makers | Joint rounds, shared protocols |
| Administrative Staff | Resource allocation | Regular meetings, data sharing |
| Support Staff | Implementation partners | Training programs, feedback sessions |
| Patients/Families | End users of care | Patient advisory councils, surveys |
| External Partners | System-wide coordination | Partnership agreements, shared metrics |
Building Effective Collaborative Relationships
Healthcare professionals often feel challenged by complex patients and the associated care needs during care transition. Interprofessional collaboration (IPC) is considered an effective approach in such situations.
Successful collaboration requires:
- Clear communication channels
- Shared goals and objectives
- Mutual respect and trust
- Regular feedback and evaluation
Patient-Centered Change Initiatives
Focusing on Patient Outcomes
All organizational change efforts must ultimately benefit patients. Interprofessional collaboration (IPC) is seen as the “gold standard” of comprehensive care, but credible evidence concerning the effects on patient-reported outcomes (PRO) is lacking.
Quality Improvement Metrics
Advanced practice nurses should track key performance indicators to measure change effectiveness:
Table 4: Key Performance Indicators for Healthcare Change Initiatives
| Category | Metrics | Target Improvements |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Safety | Medication errors, falls, infections | 20-30% reduction |
| Patient Experience | Satisfaction scores, communication ratings | 15-25% improvement |
| Clinical Outcomes | Readmission rates, mortality, length of stay | 10-20% improvement |
| Efficiency | Cost per case, resource utilization | 15-30% optimization |
Technology Integration and Innovation
Digital Health Transformation
Advanced practice nurses play crucial roles in implementing healthcare technologies:
- Electronic health records optimization
- Telehealth program development
- Clinical decision support systems
- Patient engagement platforms
Leading Innovation Initiatives
Innovation requires structured approaches:
- Idea Generation: Encouraging creative thinking across teams
- Feasibility Assessment: Evaluating technical and financial viability
- Pilot Testing: Small-scale implementation and evaluation
- Scale-Up Planning: Organization-wide rollout strategies
Professional Development and Continuous Learning
Ongoing Education Requirements
The American Association of Nurse Practitioners ® (AANP) is honored to announce the 2024 AANP Executive Leadership Program cohort. Twenty-two highly qualified nurse practitioners (NPs) were accepted into this competitive program.
Professional development opportunities include:
- Leadership certification programs
- Advanced degrees in healthcare administration
- Professional association involvement
- Mentorship relationships
Building Leadership Capabilities
The aim of this study is to explore advanced practice nurses’ perceptions of their leadership capabilities.
Key leadership development areas:
Table 5: Leadership Development Framework for Advanced Practice Nurses
| Development Area | Learning Methods | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Workshops, coaching | Improved stakeholder engagement |
| Strategic Thinking | Case studies, simulations | Enhanced planning capabilities |
| Emotional Intelligence | Self-assessment, feedback | Better team relationships |
| Financial Acumen | Training programs, mentorship | Resource management skills |
Measuring Success and Impact
Outcome Evaluation
Successful change initiatives require comprehensive evaluation:
- Process metrics (implementation milestones)
- Outcome metrics (patient and organizational results)
- Impact assessments (long-term sustainability)
Continuous Improvement Processes
Advanced practice nurses must establish systems for ongoing improvement:
- Regular data collection and analysis
- Stakeholder feedback mechanisms
- Benchmarking against industry standards
- Adaptation based on lessons learned
Challenges and Solutions in Nurse Leadership
Common Leadership Challenges
Advanced practice nurses face several obstacles in their leadership roles:
Table 6: Leadership Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Impact | Recommended Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Role Ambiguity | Unclear expectations | Job descriptions, competency frameworks |
| Resource Limitations | Constrained change capacity | Phased implementation, priority setting |
| Interprofessional Tensions | Collaboration barriers | Team building, shared governance |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex requirements | Education, compliance systems |
Building Organizational Support
Success requires strong organizational support:
- Executive sponsorship
- Adequate resource allocation
- Clear accountability structures
- Recognition and reward systems
Future Directions in Advanced Practice Nursing Leadership
Emerging Trends
The healthcare landscape continues evolving, presenting new opportunities:
- Artificial intelligence integration
- Population health management
- Value-based care models
- Global health initiatives
Preparing for Future Challenges
This article highlights the critical role of advanced practice registered nurses in the care of older adults living in nursing homes. This population is one of the frailest, marginalized, and often neglected in the United States.
Future-focused preparation includes:
- Continuous learning and adaptation
- Technology literacy development
- Global healthcare awareness
- Sustainability planning
Best Practices for Advanced Practice Nurse Leaders
Implementation Strategies
Successful nurse leaders employ proven strategies:
- Start with Why: Clearly articulate the purpose and benefits of change
- Engage Early and Often: Include stakeholders throughout the process
- Communicate Consistently: Maintain regular updates and feedback
- Celebrate Success: Recognize achievements and milestones
- Learn from Failures: Use setbacks as learning opportunities
Sustainability Planning
Long-term success requires careful planning:
- Embedding changes in policies and procedures
- Training replacement leaders
- Monitoring performance indicators
- Adapting to environmental changes
Healthcare Statistics and Impact Data
The Impact of Medical Errors
More than 7 million American patients are impacted by medical errors every year, with 7,000 to 9,000 of them dying from such mistakes, which may include medication errors and diagnostic inaccuracies.
Workforce Statistics
The nursing profession represents a significant portion of the healthcare workforce:
- Over 3.6 million registered nurses in the United States
- Projected 9% growth in nursing employment through 2030
- Increasing demand for advanced practice nurses across all settings
Table 7: Advanced Practice Nursing Growth Projections
| APRN Role | Current Numbers | Projected Growth (2024-2034) | Key Growth Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nurse Practitioners | 325,000+ | 26% | Primary care demand |
| Clinical Nurse Specialists | 70,000+ | 10% | Specialized care needs |
| Nurse Anesthetists | 44,000+ | 14% | Surgical volume increases |
| Nurse Midwives | 12,000+ | 12% | Maternal health focus |
Conclusion
Advanced practice registered nurses serve as essential change agents within healthcare organizations, driving improvements in patient care, operational efficiency, and organizational culture. Their unique combination of clinical expertise and leadership skills positions them to address complex healthcare challenges while maintaining focus on patient-centered outcomes.
Success in this role requires continuous development of leadership competencies, effective stakeholder engagement, and commitment to evidence-based practice. As healthcare continues evolving, advanced practice nurses must remain adaptable, innovative, and focused on creating positive change for patients, colleagues, and the broader healthcare industry.
The future of healthcare depends significantly on the leadership capabilities of advanced practice nurses. By embracing their roles as change agents and investing in professional development, these nursing leaders can continue driving meaningful improvements in healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
References
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2021). Nurses Leading Change – The Future of Nursing 2020-2030. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK573918/
- American Nurses Association. (2017). Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRN). Retrieved from https://www.nursingworld.org/practice-policy/workforce/what-is-nursing/aprn/
- British Journal of Nursing. (2021). Leadership and management for nurses working at an advanced level. Retrieved from https://www.magonlinelibrary.com/doi/full/10.12968/bjon.2021.30.5.282
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). Nursing Professional Development Leadership. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519064/
- American Association of Nurse Practitioners. (2024). AANP Introduces 2024 Executive Leadership Program Cohort. Retrieved from https://www.aanp.org/news-feed/aanp-introduces-2024-executive-leadership-program-cohort
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2022). The Advanced Practice Registered Nurse Leadership Role in Nursing Homes. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9066344/
- Healthcare Journal. (2023). Interprofessional Collaboration in Complex Patient Care Transition. Retrieved from https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9032/11/3/359
- BMC Health Services Research. (2022). Interprofessional collaboration and patient-reported outcomes in inpatient care. Retrieved from https://systematicreviewsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13643-022-02027-x
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2015). Interprofessional collaboration in health care. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4530359/
- TigerConnect. (2024). Benefits of Interprofessional Collaboration in Healthcare. Retrieved from https://tigerconnect.com/resources/blog-articles/5-benefits-of-interprofessional-collaboration-in-healthcare/

I am a professional nursing assignment expert offering comprehensive academic support to university nursing students across various institutions. My services are designed to help learners manage their workload effectively while maintaining academic excellence. With years of experience in nursing research, case study writing, and evidence-based reporting, I ensure every paper is original, well-researched, and aligned with current academic standards.
My goal is to provide dependable academic assistance that enables students to focus on practical training and career growth.
Contact me today to receive expert guidance and timely, high-quality nursing assignment help tailored to your academic needs.
