Explain the concept of a knowledge worker.

Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker
The term “knowledge worker” was first coined by management consultant and author Peter Drucker in his book, The Landmarks of Tomorrow (1959). Drucker defined knowledge workers as high-level workers who apply theoretical and analytical knowledge, acquired through formal training, to develop products and services. Does this sound familiar?
Nurses are very much knowledge workers. What has changed since Drucker’s time are the ways that knowledge can be acquired. The volume of data that can now be generated and the tools used to access this data have evolved significantly in recent years and helped healthcare professionals (among many others) to assume the role of knowledge worker in new and powerful ways.
In this Assignment, you will consider the evolving role of the nurse leader and how this evolution has led nurse leaders to assume the role of knowledge worker. You will prepare a PowerPoint presentation with an infographic (graphic that visually represents information, data, or knowledge. Infographics are intended to present information quickly and clearly.) to educate others on the role of nurse as knowledge worker.
Reference: Drucker, P. (1959). The landmarks of tomorrow. New York, NY: HarperCollins Publishers.
To Prepare:
- Review the concepts of informatics as presented in the Resources.
- Reflect on the role of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker.
- Consider how knowledge may be informed by data that is collected/accessed.
The Assignment:
- Explain the concept of a knowledge worker.
- Define and explain nursing informatics and highlight the role of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker.
- Include one slide that visually represents the role of a nurse leader as knowledge worker.
- Your PowerPoint should Include the hypothetical scenario you originally shared in the Discussion Forum. Include your examination of the data that you could use, how the data might be accessed/collected, and what knowledge might be derived from that data. Be sure to incorporate feedback received from your colleagues’ responses.
Below is the scenario I shared
Shift handover is a key tool in ensuring continuity of care The patient handover process in my facility is manual, and much of the data has to be written down in the patient reports. Some nurses in charge of chronic patients, however, feel that the paper work has become too much, yet the patients’ condition are the same (Smith et al., 2018).
Ms. Winnie, one of the nurses refuses to write a full patient report for a diabetes patient who has been in the facility for the last three months, claiming that we all know her needs, and we should attend to her without the written continuation instructions. She also claims that she will do the paper work once she finds free time. Before reporting Ms. Winnie to the nurse manager, I happen to realize that what she did was a grave mistake, as it would be a risk to the patient life (Anastasi, 2019).
If, for instance, the patient turnover in the facility increases during the night, and the facility hires another group of nurses to help on locum basis, it is likely that the patient whose data was not reported will not be attended to. This can lead to delay in treatment.
The involvement of clinicians is essential to developing a sustainable electronic handover system. One of the ways that a physician would use clinical judgement to form knowledge from this experience is examining possibilities. It should be understood that no one ever anticipates or prepares for medical errors (Mosadeghrad & Woldemichael, 2017). However, occurrence of experiences of negligence such as that of Ms. Winnie would increase the chances of medical error. Also, this experience is enough reason to justify the implementation of an automated system.
References
Anastasi, E. (2019). How to become a locum. Dental Nursing, 15(6), 278-280.
Mosadeghrad, A. M., & Woldemichael, A. (2017). Application of quality management in promoting patient safety and preventing medical errors. In Impact of Medical Errors and Malpractice on Health Economics, Quality, and Patient Safety (pp. 91-112). IGI Global.
Smith, J. G., Morin, K. H., Wallace, L. E., & Lake, E. T. (2018). Association of the nurse work environment, collective efficacy, and missed care. Western journal of nursing research, 40(6), 779-798.
By Day 7 of Week 2
Submit your completed Presentation.
Submission and Grading Information
To submit your completed Assignment for review and grading, do the following:
- Please save your Assignment using the naming convention “WK2Assgn+last name+first initial.(extension)” as the name.
- Click the Week 2 Assignment Rubric to review the Grading Criteria for the Assignment.
- Click the Week 2 Assignment link. You will also be able to “View Rubric” for grading criteria from this area.
- Next, from the Attach File area, click on the Browse My Computer button. Find the document you saved as “WK2Assgn+last name+first initial.(extension)” and click Open.
- If applicable: From the Plagiarism Tools area, click the checkbox for I agree to submit my paper(s) to the Global Reference Database.
- Click on the Submit button to complete your submission.
Expert Answer and Explanation

A knowledge worker is a person who collects, analyzes, and applies the analyzed information to improve processes or the organization as a whole, and in the case of nursing, to improve patient outcomes.
Nurses are considered to be knowledge workers by default. In the nursing setup, nurses are required to collect information from their patients, use the collected information to assess the needs of the patient, evaluate the best possible evidence-based intervention (data) and apply that intervention to better patient outcomes (Bergren & Maughan, 2020).
Regardless of the adoption of technology in the collection and analysis of data, it is the nurse leaders and the nursing staff who choose which data to collect from patients, and which information is useful and relevant to influence the intervention given to the patient.
Using the words of Peter Drucker, the inventor of the term, a nurse is supposed to apply both “theoretical and analytical knowledge acquired through formal training,” The application of nursing research and appreciation of evidence-based practices further emphasizes the role of nurses, as knowledge workers.
It can therefore be said that the current nursing practice cannot be isolated from concepts of collecting, applying, and generation of knowledge making nurses by default to be knowledge workers.

Nursing informatics is a field that involves the management and use of patient information using various information technology (Collins, Yen, Phillips & Kennedy, 2017). Nursing informatics has revolutionized the aspect of information management in nursing practice and plays an essential role in safe guarding patient safety and quality of care given (Mosadeghrad & Woldemichael, 2017).
Nurse informaticists use information science and technology to gather and analyze patient data to influence the provision of care and carrying out various organizational process like distribution of resources where they are needed. Therefore, it is an important emerging aspect that can prove to be strategic in nursing practice.
From the definition, there are two major features which are essential in nursing informatics. The first feature being the ability of a nurse to identify usable data, and the ability of the nurse to use technology to collect that data, manipulate and use the analyzed information to make clinical decisions. This further highlights the role of nurses as knowledge workers.
The collection of data has until recently been done manually suing the paper system (with my organization still doing the same). However, the introduction of health care systems such as EHR has made the aspect of collecting, manipulating and using data to be much easier and the accuracy of the collected data be a notch higher. This is one of the ways through which nursing informatics has been seen to help develop the nursing practice.

As indicated earlier, the application of nursing informatics further calls for nurse leaders to play an active role as knowledge workers. The first role of nurse leaders as knowledge workers is to assess usable information and collect it using health care technology to improve patient care (Bergren & Maughan, 2020).
Another role of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker is to share knowledge with other nurses on how they can improve their care delivery to patients. It is also the role of a nurse leader to generate new knowledge by conducting nursing research and through experience. The newly generated knowledge can be used to direct new and better interventions to improve quality and safety of patients. All this is facilitated by the use of nursing informatics.
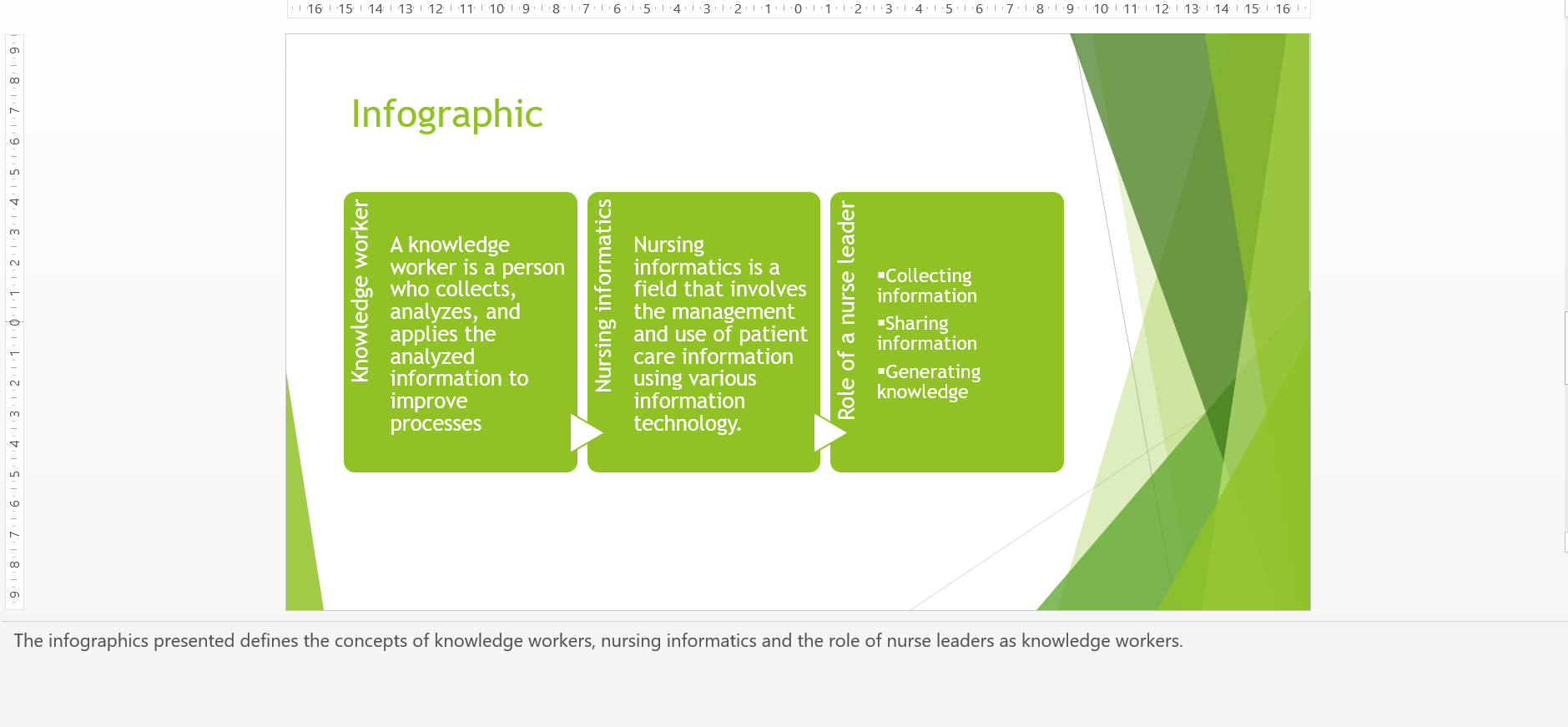
The infographics presented defines the concepts of knowledge workers, nursing informatics and the role of nurse leaders as knowledge workers.

My scenario involves Ms. Winnie who refuses to collect patient information citing that it had become redundant and tedious given the diabetic patient had been hospitalized for three months without any changes. The refusal by Ms. Winnie exposes the patient to delays in treatment and could also lead to medical errors, which informed the need to have an automated system.
Some of the data I would need to collect include data on missed care, and data on medical errors related to poor data reporting. I would also collect data from other nurses on their perception on the manual data collection system and whether the system has an impact on patient handover process. I would also collect evidence-based data detailing the application of an automated system and how it could improve patient outcomes and organizational processes.
The knowledge derived from the collected data will highlight the impact of the paper-based method in both patient outcomes and organizational efficiency. This information will be used as a basis to inform the need to have an automated system.
References
Bergren, M. D., & Maughan, E. D. (2020). Data and information literacy: A fundamental nursing competency. NASN School Nurse, 35(3), 140-142. https://doi.org/10.1177/1942602X20913249
Collins, S., Yen, P. Y., Phillips, A., & Kennedy, M. K. (2017). Nursing informatics competency assessment for the nurse leader: The Delphi study. JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration, 47(4), 212-218. doi: 10.1097/NNA.0000000000000467
Mosadeghrad, A. M., & Woldemichael, A. (2017). Application of quality management in promoting patient safety and preventing medical errors. In Impact of Medical Errors and Malpractice on Health Economics, Quality, and Patient Safety (pp. 91-112). IGI Global.
Drucker, P. (1959). The landmarks of tomorrow. New York, NY: HarperCollins Publishers.
Place your order now for a similar assignment and get fast, cheap and best quality work written by our expert level assignment writers. Use Coupon Code: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Use Coupon Code: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
FAQs
Highlight the role of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker
As a knowledge worker, a nurse leader is responsible for managing and utilizing information and knowledge to improve patient care outcomes and organizational performance. The following are some key roles of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker:
- Knowledge Acquisition: Nurse leaders need to continuously acquire knowledge and stay up-to-date with the latest developments in healthcare practices, policies, and technologies. They need to keep abreast of new research findings and best practices and evaluate their relevance to their organization’s goals.
- Knowledge Creation and Sharing: Nurse leaders are responsible for creating new knowledge through research, clinical trials, and quality improvement initiatives. They also share this knowledge with other healthcare professionals, patients, and families to promote evidence-based practice and improve patient outcomes.
- Decision-making: Nurse leaders use their knowledge and expertise to make informed decisions about patient care, resource allocation, and organizational strategy. They analyze data, evaluate outcomes, and assess risks to make sound decisions that promote the best interests of patients and the organization.
- Collaboration: Nurse leaders work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals to create and implement policies and procedures that promote quality care and patient safety. They share their knowledge and expertise with other healthcare providers and work together to improve patient outcomes.
- Leadership: Nurse leaders use their knowledge and skills to lead and inspire their teams to achieve organizational goals. They create a positive work environment that fosters collaboration, communication, and innovation. They also mentor and train other nurses to help them develop their knowledge and skills.
In summary, nurse leaders play a critical role as knowledge workers in healthcare organizations. They acquire, create, share, and apply knowledge to improve patient outcomes, promote evidence-based practice, and achieve organizational goals.
The Nurse Leader as a Knowledge Worker
In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, nurse leaders play a pivotal role not only in patient care but also as knowledge workers who harness, manage, and disseminate valuable information. As healthcare becomes increasingly data-driven and complex, nurse leaders must embrace their roles as knowledge workers to drive informed decision-making, promote best practices, and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Introduction
Nurse leaders, occupying influential positions in healthcare organizations, are at the forefront of decision-making and patient care coordination. As healthcare transforms into a data-rich environment, nurse leaders are challenged to leverage their skills as knowledge workers to navigate this landscape effectively.
Defining the Knowledge Worker in Healthcare
A knowledge worker is an individual who manages, creates, and disseminates information to enhance productivity and contribute to the organization’s success. In healthcare, nurse leaders exemplify this role by using their clinical expertise and strategic thinking to make informed decisions and ensure the delivery of high-quality care.
The Multifaceted Role of Nurse Leaders
Nurse leaders wear many hats, from clinical experts and educators to managers and innovators. Their role as knowledge workers involves:
Curating and Utilizing Evidence-Based Practices
Nurse leaders critically evaluate research, guidelines, and best practices to inform clinical decisions. They ensure that their teams are aligned with evidence-based approaches to deliver safe and effective care.
Facilitating Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication is crucial in healthcare. Nurse leaders bridge the gap between different departments and stakeholders, ensuring that information flows seamlessly to support coordinated care.
Navigating Technological Advancements
Healthcare technology evolves rapidly. Nurse leaders embrace new tools and systems, promoting their integration to enhance patient care, data management, and communication.
Embracing Lifelong Learning
Nurse leaders recognize that knowledge is ever-evolving. They lead by example, pursuing continuous learning to stay updated on the latest advancements and trends.
Leading with Vision and Strategy
As knowledge workers, nurse leaders develop strategic initiatives that align with the organization’s goals. They envision the future of healthcare and drive their teams toward that vision.
Conclusion
In an information-driven era, nurse leaders serve as invaluable knowledge workers who harness their expertise to transform healthcare delivery. By championing evidence-based practices, facilitating communication, adapting to technology, and fostering a culture of continuous learning, nurse leaders empower their teams to provide exceptional patient care and contribute to the advancement of healthcare as a whole.
FAQ 1:
How do nurse leaders balance their clinical duties with their role as knowledge workers?
- Nurse leaders often delegate certain clinical responsibilities to focus on strategic decision-making and knowledge management. Delegation and effective time management are key.
FAQ 2:
What are some challenges nurse leaders face in adopting technology for information management?
- Nurse leaders may encounter resistance to change, technical barriers, or concerns about patient privacy. Addressing these challenges requires effective communication and training.
FAQ 3:
How can nurse leaders encourage a culture of continuous learning among their teams?
- Nurse leaders can promote learning through mentorship, providing opportunities for education and skill development, and recognizing and rewarding a commitment to learning.
FAQ 4:
What impact does the role of a knowledge worker have on patient-centered care?
- The role of a knowledge worker enhances patient-centered care by ensuring that decisions are evidence-based, informed, and aligned with best practices, resulting in improved patient outcomes.
FAQ 5:
Are there specific certifications or training programs for nurse leaders to enhance their knowledge management skills?
- Yes, there are various certifications and training programs that focus on leadership, management, and knowledge management in healthcare. These include Nurse Leadership certifications and courses on healthcare informatics.
The Role of Nursing Informatics in Nursing Leadership
Nursing leadership in today’s healthcare landscape extends far beyond traditional management roles. With the rapid integration of technology into healthcare systems, nursing informatics has emerged as a vital component of nursing leadership. This dynamic field bridges the gap between healthcare, technology, and patient-centered care, empowering nurse leaders to make informed decisions, enhance workflow efficiency, and elevate the overall quality of patient care.
Introduction
Nursing leadership has evolved to encompass roles that are not only focused on management but also on leveraging technology to enhance patient care. Nursing informatics blends the expertise of nursing professionals with the power of technology, enabling nurse leaders to navigate the complexities of modern healthcare effectively.
Understanding Nursing Informatics
Nursing informatics involves the integration of information science, computer science, and nursing science to manage and communicate data, information, and knowledge in nursing practice. It encompasses various aspects, including electronic health records, clinical decision support systems, and health information exchange.
The Intersection of Nursing Informatics and Leadership
Nurse leaders equipped with nursing informatics knowledge possess a unique advantage. Their roles extend beyond administrative duties to encompass strategic decision-making involving technology integration, data utilization, and workflow optimization.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Patient Care
Nursing informatics empowers nurse leaders to implement and optimize technologies that directly impact patient care. This includes electronic health records that ensure accurate and accessible patient information, leading to safer and more effective care.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Nurse leaders adept in nursing informatics can harness data to make informed decisions. Analyzing trends and patterns allows them to proactively address challenges, allocate resources efficiently, and design evidence-based interventions.
Promoting Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Nursing informatics fosters collaboration between different healthcare disciplines. Nurse leaders facilitate the integration of technology solutions that streamline communication and data sharing, leading to improved interdisciplinary teamwork.
Ensuring Patient Privacy and Security
Nurse leaders play a crucial role in safeguarding patient information. They develop and enforce policies that adhere to strict privacy regulations, ensuring that patient data remains confidential and secure.
Embracing Change and Innovation
Nursing informatics encourages nurse leaders to embrace innovation and adapt to technological advancements. By staying current with emerging trends, nurse leaders can drive transformative change within their organizations.
Conclusion
Nursing informatics has become an essential tool for nursing leadership, reshaping the way healthcare is delivered. Nurse leaders who embrace this field can harness the power of technology to enhance patient care, optimize workflows, and make data-driven decisions that positively impact both patients and healthcare systems.
FAQsFAQ 1:
What skills are essential for nurse leaders to excel in nursing informatics?
- Nurse leaders should possess a strong foundation in nursing practice, technology literacy, analytical thinking, and effective communication to excel in nursing informatics.
FAQ 2:
How does nursing informatics impact clinical workflows?
- Nursing informatics streamlines clinical workflows by optimizing processes, enhancing communication, and ensuring the seamless flow of information between healthcare team members.
FAQ 3:
What is the role of nurse leaders in ensuring data security and privacy?
- Nurse leaders establish protocols, train staff, and implement technologies to ensure that patient data remains secure and compliant with privacy regulations.
FAQ 4:
Can nursing informatics improve patient outcomes and satisfaction?
- Yes, nursing informatics can lead to improved patient outcomes by facilitating accurate and timely data sharing, supporting evidence-based practice, and enhancing communication among healthcare providers.
FAQ 5:
Are there specialized certifications for nurse leaders in nursing informatics?
- Yes, there are certifications such as the ANCC Nursing Informatics board certification that validate a nurse leader’s expertise in nursing informatics and technology integration.
Understanding the Concept of Knowledge Worker
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern work, the concept of a knowledge worker has gained significant prominence. Coined by management guru Peter Drucker, the term refers to individuals whose primary role involves the acquisition, creation, and application of knowledge to drive productivity and innovation. This article delves into the intricacies of the knowledge worker concept, its implications across various industries, and its pivotal role in shaping the information age.
Introduction
In the digital era, where information is a valuable currency, the concept of a knowledge worker has emerged as a cornerstone of modern labor. Knowledge workers differ from traditional manual laborers, as their contributions revolve around intellectual capital and the application of insights to solve complex challenges.
Defining Knowledge Workers
Knowledge workers are individuals who leverage their expertise, insights, and creativity to add value to their organizations. Their roles span various sectors, including business, technology, healthcare, education, and beyond. Unlike routine tasks, their responsibilities require critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to adapt swiftly to changing circumstances.
Key Characteristics of Knowledge Workers
- Intellectual Capital: Knowledge workers possess intellectual assets, such as expertise, experiences, and insights, which they utilize to innovate and create.
- Continuous Learning: Embracing lifelong learning is a hallmark of knowledge workers, as they strive to remain updated with the latest trends and developments.
- Autonomy: These workers often have autonomy over their work processes and decisions, enabling them to navigate complex challenges with flexibility.
- Problem-Solving: Knowledge workers excel in analyzing intricate problems and formulating solutions by leveraging their expertise and creativity.
- Collaboration: While they work independently, knowledge workers also thrive in collaborative environments, sharing insights to drive collective progress.
Knowledge Workers in the Information Age
The concept of knowledge workers has gained prominence due to the information age’s reliance on data, insights, and innovation. In this era, the ability to access, synthesize, and apply knowledge holds immense value and is often a decisive factor for organizational success.
Evolving Roles and Industries
The concept of knowledge workers transcends industries. In business, they drive strategic decision-making; in technology, they innovate solutions; in healthcare, they provide evidence-based care; and in education, they cultivate critical thinking. The roles may differ, but the core principle of leveraging knowledge remains constant.
Nurturing a Culture of Knowledge
Organizations that recognize the significance of knowledge workers invest in fostering a culture of continuous learning. They provide resources, opportunities for skill development, and platforms for idea exchange to empower their knowledge workers.
Challenges and Opportunities
While knowledge workers play a pivotal role, challenges such as information overload, burnout, and keeping up with rapid changes can arise. However, these challenges also present opportunities for growth, adaptation, and resilience.
Conclusion
In the age of information, knowledge workers are the driving force behind innovation, problem-solving, and progress. As industries continue to evolve, the concept of the knowledge worker will remain indispensable, reshaping the nature of work and emphasizing the importance of continuous learning, creativity, and the strategic application of insights.
FAQ 1:
Are all professionals considered knowledge workers?
- While many professionals have knowledge-based aspects in their roles, true knowledge workers are those whose primary contributions involve the creation, application, and dissemination of knowledge.
FAQ 2:
How does technology impact the role of knowledge workers?
- Technology amplifies the impact of knowledge workers by providing tools for efficient information management, collaboration, and the rapid dissemination of insights.
FAQ 3:
What skills are essential for thriving as a knowledge worker?
- Skills such as critical thinking, adaptability, communication, collaboration, and a commitment to continuous learning are essential for success as a knowledge worker.
FAQ 4:
Can organizations benefit from investing in knowledge worker development?
- Absolutely. Organizations that prioritize knowledge worker development can foster innovation, improve decision-making, and drive overall productivity and growth.
FAQ 5:
How does the concept of knowledge workers relate to lifelong learning?
- The concept of knowledge workers aligns closely with lifelong learning, as continuous learning is a cornerstone of their roles. Staying updated with the latest knowledge and trends is essential for their effectiveness.

I am a professional nursing assignment expert offering comprehensive academic support to university nursing students across various institutions. My services are designed to help learners manage their workload effectively while maintaining academic excellence. With years of experience in nursing research, case study writing, and evidence-based reporting, I ensure every paper is original, well-researched, and aligned with current academic standards.
My goal is to provide dependable academic assistance that enables students to focus on practical training and career growth.
Contact me today to receive expert guidance and timely, high-quality nursing assignment help tailored to your academic needs.


