Table of Contents
TogglePost a description of at least one potential benefit of using big data as part of a clinical system and explain why
Big Data risks and Rewards
When you wake in the morning, you may reach for your cell phone to reply to a few text or email messages that you missed overnight. On your drive to work, you may stop to refuel your car. Upon your arrival, you might swipe a key card at the door to gain entrance to the facility. And before finally reaching your workstation, you may stop by the cafeteria to purchase a coffee.
From the moment you wake, you are in fact a data-generation machine. Each use of your phone, every transaction you make using a debit or credit card, even your entrance to your place of work, creates data. It begs the question: How much data do you generate each day? Many studies have been conducted on this, and the numbers are staggering: Estimates suggest that nearly 1 million bytes of data are generated every second for every person on earth.
As the volume of data increases, information professionals have looked for ways to use big data—large, complex sets of data that require specialized approaches to use effectively. Big data has the potential for significant rewards—and significant risks—to healthcare. In this Discussion, you will consider these risks and rewards.
To Prepare:
- Review the Resources and reflect on the web article Big Data Means Big Potential, Challenges for Nurse Execs .
- Reflect on your own experience with complex health information access and management and consider potential challenges and risks you may have experienced or observed.
Post a description of at least one potential benefit of using big data as part of a clinical system and explain why. Then, describe at least one potential challenge or risk of using big data as part of a clinical system and explain why. Propose at least one strategy you have experienced, observed, or researched that may effectively mitigate the challenges or risks of using big data you described. Be specific and provide examples.
Big Data Risks and Rewards: Sample Answer
The Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS), Patient Portals are some of the examples of the clinical system that generate data which providers can leverage to support decision-making. In clinical settings, data is crucial in the sense that it allows providers to identify the appropriate intervention based on patient’s needs or characteristics such as their past health information, and their demographic background (Awrahman et al., 2022). In healthcare, big data represents large volume of data collected using the clinical systems, and which support the delivery of care. While this kind of data is associated with various benefits, its use poses certain risks that are worth examining.
Potential Benefit of using Big Data as Part of Clinical System
A key benefit of big data is that it has the potential of helping reduce adverse health events linked to medical errors. This is because analyzing this data using data analytics makes it possible for one to determine the trend of a disease or how it develops. The data analytics technology, for example, analyzes data, identifying the factors that increase the risk of medication error. Through this prediction, a provider can take appropriate measures to avert the risk of error (Dicuonzo et al., 2022). In addition, data can inform the intervention that is likely to translate into better health outcomes, lessening the possibility of choosing inappropriate intervention.
Potential Challenge or Risk of using Big Data as Part of the Clinical System
While the use of big data provides significant opportunities for providers to make decisions that optimize the quality of health outcomes, its use poses serious concerns part of which is data security threat. One of the key reasons for this is that hackers can hack into the clinical systems, accessing this data which include information such as clients’ personal details (Dicuonzo et al., 2022). This threat is high in a scenario in which members of the staff are ill equipped with adequate data security knowledge. In this kind of a situation, they may use weak passwords, increasing the threat of intrusion into the systems that store this data. Additionally, practices such as failure to firewalls can cause data security issues.
The Strategy for Mitigating the Risks of using Big Data
For an organization to cushion itself against the breach of security, it needs to conduct data security training with emphasis on educating its staff about the best practices in data management. Part of this training involves educating the staff how to use secure passwords while stressing the importance of compliance with the legal requirements linked to data privacy and confidentiality. When engaging the employees in training, one would equally need to emphasize the ethical and legal implications associated with breach of data privacy (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2022). Ensuring data security is crucial in the sense that it cushions the organization against lawsuits and negative reputation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, utilization of big data provides significant benefits when it comes to the delivery of care considering that it lessens the risk of medical errors as it allows clinicians to identify an intervention that is likely to help lead to better health outcomes based on the patient’s needs. However, the challenge of using large amount of data to inform clinical decisions increases the risk of data breach. To avert this problem, a hospital should train its staff, allowing them to learn the data security strategies.
References
Awrahman, B. J., Aziz Fatah, C., & Hamaamin, M. Y. (2022). A Review of the Role and Challenges of Big Data in Healthcare Informatics and Analytics. Computational intelligence and neuroscience, 2022, 5317760. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5317760.
Dicuonzo, G., Galeone, G., Shini, M., & Massari, A. (2022). Towards the Use of Big Data in Healthcare: A Literature Review. Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland), 10(7), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10071232.
McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. G. (2022). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge (5th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Alternative Verified Answer
Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics is a term used in healthcare that describes the collection and analysis of large amounts of data collected through various channels to facilitate clinical decision-making. Big data analytics encompasses data collected from social media, wearable and tracking devices, biometrics, and transactional information, to list a few collected from patients and the public. Big data analytics continue to redefine the healthcare industry and support clinical decision-making by providing better accuracy, among other advantages that will be discussed.
Benefits of Using Big Data
- One benefit of big data is improved clinical decision-making. Big data analysis allows clinicians to make evidence-based patient-specific assessments and predictions, leading to better and more accurate interventions and decisions made within the clinical setting.
- Big data also helps to reduce the number of medical errors within clinical settings. By analyzing data from electronic health records, big data can help clinicians flag suspicious entries or medication prescriptions that could lead to medication errors.
- Big data can also help reduce healthcare costs by reducing some of the redundancies within care settings and identifying where there is wastage or preventable loss of resources within the care delivery chain (Badr et al., 2024).
- Big data can also enhance patient experience by predicting patient preferences and allowing clinicians to customize care based on those preferences. For example, data collected through patient feedback can help create quality improvement interventions to enhance patient interactions.
Challenges of Using Big Data
Several challenges come with using big data in clinical settings.
- The first challenge is data privacy and security. The collection of big data has been contentious for some time due to issues concerning the privacy and security of the data collected, some of which have patient-identifiable information. This information may be put at risk when unauthorized persons access it through mischievous means, such as cyberattacks (Seh et al., 2020).
- Another risk of using big data is the collection of inaccurate or incomplete information. Data collected without proper checking and cleaning can lead to incomplete or misleading information being stored and later used to inform decision-making. Using such data can lead to inaccurate decision-making, which can have serious consequences on patient outcomes (Norori et al., 2021).
- The third risk concerns the consolidation of big data into a single repository, especially when data is coming for different sources and in different formats, which makes it difficult to analyze and use the data for clinical decision-making.
Strategies to Mitigate the Listed Challenges
- One strategy that could help mitigate the challenge associated with the privacy and security of data collected is deploying strong cyber security measures. For example, the use of firewalls, strong authentication systems, and antiviruses may prevent access to the database through malicious means (Seh et al., 2020).
- Another strategy is the use of data automation tools to help with data cleaning and organizing making it easier to store the data in a format that is uniform and easy to analyze. Organizations are also currently using AI tools to help with data integration and storage, where poor-quality data that is either inaccurate or incomplete is eliminated before storage (Norori et al., 2021).
- The third strategy is the use of data integration tools. These are tools that can identify the type of data collected, arrange them based on similarities, and store them in tables for easy retrieval and analysis.
The application of big data is expected to continue revolutionizing healthcare by improving the quality of clinical decisions and overall patient care. Addressing the challenges and risks attached to big data application is critical to its adoption in clinical settings.
References
Badr, Y., Kader, L. A., & Shamayleh, A. (2024). The use of big data in personalized healthcare to reduce inventory waste and optimize patient treatment. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(4), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040383
Norori, N., Hu, Q., Aellen, F. M., Faraci, F. D., & Tzovara, A. (2021). Addressing bias in big data and AI for health care: A call for open science. Patterns, 2(10), 100347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2021.100347
Seh, A. H., Zarour, M., Alenezi, M., Sarkar, A. K., Agrawal, A., Kumar, R., & Khan, R. A. (2020). Healthcare data breaches: insights and implications. Healthcare, 8(2), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8020133
Place your order now for a similar assignment and get fast, cheap and best quality work written by our expert level assignment writers. Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Use Coupon: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order

Big Data in Healthcare: Transforming Medical Care Through Advanced Analytics
Introduction
The healthcare industry is experiencing an unprecedented digital transformation, with big data emerging as a cornerstone of modern medical practice. As healthcare systems worldwide generate massive volumes of information daily, the ability to harness, analyze, and derive actionable insights from this data has become critical for improving patient outcomes, reducing costs, and advancing medical research.
What is Big Data in Healthcare?
Big data in healthcare refers to the vast, complex datasets generated by healthcare systems, medical devices, electronic health records (EHRs), clinical trials, genomic sequencing, and various other sources within the medical ecosystem. These datasets are characterized by the traditional “4 Vs” of big data:
- Volume: The sheer amount of data generated daily across healthcare systems
- Velocity: The speed at which healthcare data is created and processed
- Variety: The diverse types of data, including structured (databases) and unstructured (images, notes)
- Veracity: The accuracy and reliability of healthcare information
Healthcare big data encompasses multiple sources including patient records, medical imaging, laboratory results, prescription data, insurance claims, clinical trial data, genomic information, and real-time monitoring data from wearable devices and IoT medical equipment.
The scale of healthcare data generation is staggering. According to recent industry analysis, a single hospital can generate approximately 50 petabytes of patient and operational data per day. The healthcare industry’s data generation is expected to grow at an exponential rate, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 35% through 2025.
Benefits of Big Data in Healthcare
Enhanced Patient Care and Outcomes
Big data analytics enables healthcare providers to deliver more personalized and effective care. By analyzing comprehensive patient datasets, medical professionals can identify patterns that lead to better diagnosis accuracy, treatment optimization, and prevention strategies. Predictive analytics models can identify patients at risk for complications, enabling proactive interventions that improve outcomes and reduce mortality rates.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Healthcare organizations leverage big data to optimize their operations, from resource allocation to staff scheduling. Data analytics helps hospitals predict patient admission rates, optimize bed utilization, and streamline supply chain management. For example, the Gundersen Health System used predictive analytics powered by artificial intelligence to increase room utilization by 9%.
Cost Reduction and Financial Optimization
Big data analytics contributes significantly to healthcare cost reduction by identifying inefficiencies, preventing unnecessary procedures, and reducing readmission rates. The market for health-related financial analytics services using big data is predicted to reach over $13 billion by 2025, highlighting the substantial economic impact of these technologies.
Accelerated Medical Research and Drug Discovery
Big data facilitates faster drug discovery and development by analyzing vast datasets from clinical trials, genomic studies, and real-world evidence. Machine learning algorithms can identify potential drug candidates, predict treatment responses, and accelerate the path from laboratory to patient.
Population Health Management
Healthcare organizations use big data to monitor and improve population health outcomes. By analyzing data across large patient populations, public health officials can identify disease trends, track epidemic patterns, and implement targeted prevention programs.
Big Data in Healthcare Examples
Predictive Analytics for Disease Prevention
Healthcare systems are implementing sophisticated predictive models to identify patients at risk for various conditions. For instance, cardiovascular disease prediction models analyze patient age, chronic illnesses, and medication adherence to identify individuals with the highest probability of hospitalization. These insights enable healthcare providers to implement preventive measures and reduce acute care episodes.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Genomic data analysis allows for precision medicine approaches where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles. By combining genomic and transcriptomic data with proteomic and metabolomic information, healthcare providers can develop highly personalized treatment strategies that maximize efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
Real-time Patient Monitoring
Wearable devices and IoT sensors continuously collect patient data, enabling real-time health monitoring. This continuous data stream allows for immediate detection of health deterioration, medication adherence monitoring, and chronic disease management outside traditional clinical settings.
Medical Image Analysis
Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms analyze medical images with unprecedented accuracy. These systems can detect early-stage cancers, identify fractures, and diagnose neurological conditions more quickly and accurately than traditional methods.
Hospital Readmission Reduction
Predictive models analyze patient data to identify individuals at high risk for readmission. By implementing targeted interventions for these patients, hospitals have successfully reduced readmission rates while improving patient satisfaction and outcomes.
What is the Role of Data Analytics in Healthcare?
Data analytics serves as the bridge between raw healthcare data and actionable insights that improve patient care and operational efficiency. The role encompasses several critical functions:
Descriptive Analytics
This foundational level of analytics answers “what happened” by analyzing historical data to understand past trends, patterns, and outcomes. Healthcare organizations use descriptive analytics to track key performance indicators, monitor quality metrics, and assess operational performance.
Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics goes deeper to answer “why did it happen” by identifying the root causes of specific outcomes or trends. This analysis helps healthcare providers understand the factors contributing to patient complications, operational inefficiencies, or quality issues.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics forecasts future outcomes based on historical and real-time data. In healthcare, this capability is revolutionary, enabling providers to anticipate patient deterioration, predict disease outbreaks, forecast resource needs, and identify patients likely to benefit from specific interventions.
Prescriptive Analytics
The most advanced form of analytics, prescriptive analytics, recommends specific actions to achieve desired outcomes. This includes treatment recommendations, resource allocation strategies, and operational optimization suggestions based on comprehensive data analysis.
Clinical Decision Support
Data analytics powers clinical decision support systems that provide healthcare providers with evidence-based recommendations at the point of care. These systems analyze patient data against vast medical knowledge databases to suggest diagnoses, treatments, and care protocols.
Big Data in Healthcare Management: Analysis and Future Prospects
Current Market Landscape
The global big data in healthcare market has experienced remarkable growth. The market size was estimated at $56.53 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.41% through 2033. Some projections suggest the market could reach $540 billion by 2035, representing a dramatic expansion from $67 billion in 2023.
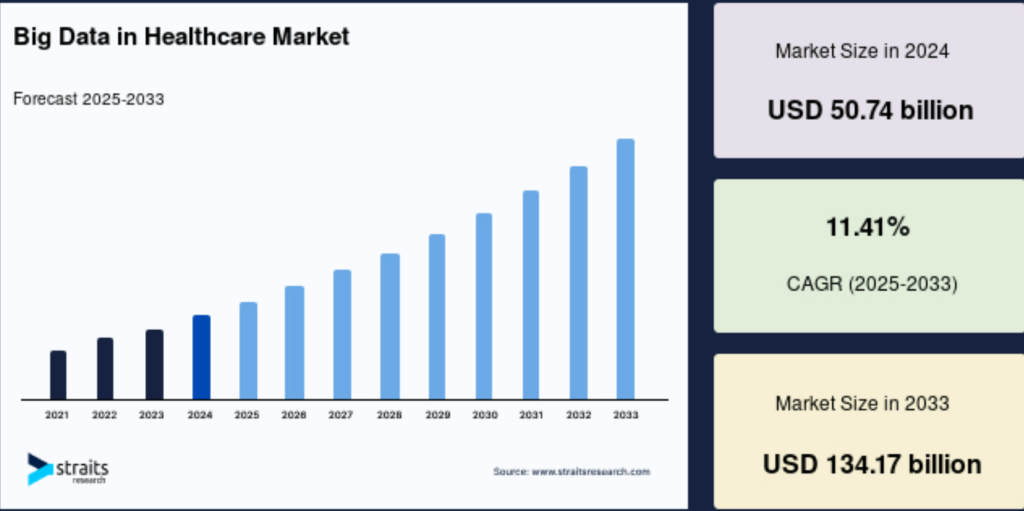
This growth is driven by several factors including the increasing adoption of electronic health records, the proliferation of connected medical devices, growing demand for personalized medicine, and the need for healthcare organizations to improve operational efficiency while reducing costs.
Technological Advancements
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with big data analytics is creating unprecedented opportunities for healthcare innovation. Natural language processing enables the analysis of unstructured clinical notes, while computer vision algorithms revolutionize medical imaging analysis.
Cloud computing infrastructure has made advanced analytics more accessible to healthcare organizations of all sizes, enabling smaller hospitals and clinics to leverage sophisticated data analytics capabilities previously available only to large health systems.
Genomic Data Integration
The convergence of big data analytics with genomic medicine represents a frontier of enormous potential. By 2025, the number of human genomes sequenced could reach between 100 million to 2 billion, creating massive datasets that, when combined with clinical data, will enable unprecedented precision in medical treatment.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite the tremendous potential, big data in healthcare faces significant challenges including data privacy concerns, interoperability issues, data quality problems, and the need for specialized expertise. Healthcare organizations are addressing these challenges through robust cybersecurity measures, standardized data formats, and comprehensive staff training programs.
Future Prospects
The future of big data in healthcare points toward several transformative developments:
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI will become increasingly sophisticated in analyzing complex healthcare datasets, enabling more accurate diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
Real-time Analytics: The capability to process and analyze data in real-time will enable immediate clinical interventions and proactive health management.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Connected medical devices will generate continuous data streams, creating comprehensive patient health profiles that enable preventive care approaches.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain may address data security and interoperability challenges while maintaining patient privacy and data integrity.
Quantum Computing: As quantum computing becomes more accessible, it will enable the analysis of exponentially larger datasets, potentially revolutionizing drug discovery and genomic analysis.
How Does Departmental and Financial Data Play into Healthcare Data Analytics?
Departmental Data Integration
Healthcare organizations generate data across multiple departments, each contributing unique insights to the overall analytics ecosystem:
Clinical Departments: Generate patient care data including diagnoses, treatments, outcomes, and clinical notes that form the foundation of care quality analytics.
Laboratory Services: Produce test results and diagnostic data that are crucial for disease identification, treatment monitoring, and research applications.
Radiology: Creates vast amounts of imaging data that, when analyzed with advanced algorithms, can improve diagnostic accuracy and speed.
Pharmacy: Contributes medication data that enables drug interaction analysis, adherence monitoring, and pharmaceutical outcomes research.
Emergency Services: Generates real-time patient data that can inform predictive models for patient flow and resource allocation.
Financial Data Analytics
Financial data represents a critical component of healthcare analytics, encompassing multiple dimensions:
Revenue Cycle Management: Analytics optimize billing processes, reduce claim denials, and improve collection rates by identifying patterns in payment delays and denials.
Cost Analysis: Detailed cost analytics help healthcare organizations understand the true cost of care delivery, identify cost-saving opportunities, and optimize resource allocation.
Payer Analytics: Analysis of insurance and reimbursement data helps organizations negotiate better contracts and understand payment patterns.
Value-Based Care Metrics: Financial analytics support the transition to value-based care models by tracking outcomes relative to costs and identifying opportunities for improvement.
Integrated Analytics Approach
The most effective healthcare analytics strategies integrate departmental and financial data to create comprehensive insights:
Operational Efficiency: Combining clinical and financial data reveals opportunities to reduce costs while maintaining or improving care quality.
Resource Optimization: Integrated analytics help organizations allocate resources more effectively by understanding both clinical needs and financial constraints.
Quality Improvement: Financial incentives for quality care can be optimized through analytics that track both clinical outcomes and associated costs.
Strategic Planning: Comprehensive data analysis supports long-term strategic decisions about service lines, facility investments, and market expansion.
Performance Measurement
Healthcare organizations use integrated departmental and financial analytics to measure performance across multiple dimensions:
Clinical Quality Metrics: Track patient outcomes, safety indicators, and care effectiveness measures.
Financial Performance Indicators: Monitor revenue growth, cost management, and profitability across different service lines.
Operational Efficiency Measures: Assess resource utilization, workflow optimization, and process improvement opportunities.
Patient Satisfaction Scores: Analyze patient experience data in conjunction with clinical and financial outcomes.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
The healthcare industry faces unique challenges in protecting sensitive patient information while leveraging big data analytics. The importance of robust security measures is underscored by recent data breach statistics showing that in 2024, there were 14 data breaches involving more than 1 million healthcare records, with the largest affecting an estimated 190 million individuals.
Healthcare organizations must implement comprehensive security frameworks that include encryption, access controls, audit trails, and staff training to protect patient data while enabling analytics capabilities. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe is essential for maintaining patient trust and avoiding legal penalties.
Conclusion
Big data in healthcare represents a transformative force that is reshaping how medical care is delivered, managed, and optimized. With the global market expected to reach extraordinary growth levels and data generation accelerating exponentially, healthcare organizations that effectively harness big data analytics will gain significant competitive advantages in improving patient outcomes, reducing costs, and advancing medical knowledge.
The integration of departmental and financial data creates comprehensive analytics capabilities that enable healthcare organizations to make data-driven decisions across all aspects of their operations. As technology continues to advance and new data sources emerge, the potential for big data to revolutionize healthcare will only continue to expand.
Success in leveraging big data requires a strategic approach that addresses technological capabilities, data governance, security requirements, and organizational change management. Healthcare leaders who invest in these capabilities today will be positioned to deliver superior patient care and operational excellence in the data-driven future of healthcare.
References
- Straits Research. (2025). Big Data in Healthcare Market Size, Global Trends, Share, Forecast to 2033. https://straitsresearch.com/report/big-data-in-healthcare-market
- Statista. (2025). Global big data in healthcare market size 2016 & 2025.
- Journal of Big Data. (2019). Big data in healthcare: management, analysis and future prospects.
- Edge Delta. (March 2025). Big Data In Healthcare Statistics: Trends and Market Insights. https://edgedelta.com/company/blog/big-data-in-healthcare-industy-overview
- HIPAA Journal. (March 2025). The Biggest Healthcare Data Breaches of 2024.
- World Health Organization Europe. (2021). Using big data to inform health care: opportunities, challenges and considerations.
- Globe Newswire. (2024). Global Big Data in Healthcare Market, Trends and Forecasts Report 2024. https://tinyurl.com/y56xks83
- Roots Analysis. (March 2025). Big Data in Healthcare Market Size, Growth Trends 2035.
- American Health Information Management Association Journal. (February 2024). Using Data Analytics to Predict Outcomes in Healthcare.
- Reveal BI. (February 2025). Predictive Analytics In Healthcare.
- TechTarget Health Tech Analytics. 10 high-value use cases for predictive analytics in healthcare.
- Segment Data Hub. Predictive Analytics in Healthcare: Use Cases & Examples.
Weekly Resources
- McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. G. (2022). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge (5th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning.
- Chapter 22, “Data Mining as a Research Tool” (pp. 537-558)
- Chapter 24, “Bioinformatics, Biomedical Informatics, and Computational Biology” (pp. 581-588)
- Glassman, K. S. (2017). Using data in nursing practiceLinks to an external site.. American Nurse Today, 12(11), 45–47. Retrieved from https://www.americannursetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/ant11-Data-1030.pdf
- Thew, J. (2016, April 19). Big data means big potential, challenges for nurse execs Links to an external site.. Retrieved from https://www.healthleadersmedia.com/nursing/big-data-means-big-potential-challenges-nurse-execs
- Wang, Y., Kung, L., & Byrd, T. A. (2018). Big data analytics: Understanding its capabilities and potential benefits for healthcare organizationsLinks to an external site.. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 126 (1), 3–13.
- Walden University, LLC. (Executive Producer). (2012). Data, information, knowledge and wisdom continuum Links to an external site. [Multimedia file]. Baltimore, MD: Author. Retrieved from http://cdn-media.waldenu.edu/2dett4d/Walden/NURS/6051/03/mm/continuum/index.html
- Walden University, LLC. (Producer). (2018). Health Informatics and Population Health: Analyzing Data for Clinical Success [Video file]. Baltimore, MD: Author.

I am a professional nursing assignment expert offering comprehensive academic support to university nursing students across various institutions. My services are designed to help learners manage their workload effectively while maintaining academic excellence. With years of experience in nursing research, case study writing, and evidence-based reporting, I ensure every paper is original, well-researched, and aligned with current academic standards.
My goal is to provide dependable academic assistance that enables students to focus on practical training and career growth.
Contact me today to receive expert guidance and timely, high-quality nursing assignment help tailored to your academic needs.



